2025全面解析Claude API速率限制:详细解决方案与优化技巧
本文深入分析Claude API速率限制机制,提供8种专业解决方案,包括中转服务、重试机制和代码优化,帮助开发者高效突破API限制,提升应用性能。
Nano Banana Pro
4K图像官方2折Google Gemini 3 Pro Image · AI图像生成
2025全面解析Claude API速率限制:详细解决方案与优化技巧
{/* 封面图片 */}
🔥 2025年6月实测有效:本文详细分析了Claude API的速率限制机制,提供8种专业解决方案,包括使用laozhang.ai中转服务、实现智能重试策略、优化代码结构等,全面帮助开发者突破API限制瓶颈!
作为AI领域的佼佼者,Anthropic的Claude API以其卓越的能力和丰富的功能备受开发者青睐。然而,随着项目规模扩大和用户增长,许多开发者开始面临一个共同的挑战:Claude API的速率限制(Rate Limit)。当你的应用在短时间内发送过多请求时,很容易触发"429 Too Many Requests"错误,这不仅影响用户体验,还可能导致业务中断。
本文将深入解析Claude API的速率限制机制,并提供8种经过验证的解决方案,帮助开发者高效突破这些限制,构建更稳定、更可靠的AI应用。无论你是遇到了偶尔的429错误,还是需要大规模处理并发请求,这里都能找到适合你的方案。
目录
Claude API速率限制详解
要解决Claude API的速率限制问题,首先需要深入了解其限制机制的工作原理。Anthropic采用多层次的速率限制策略,旨在保护API服务的稳定性和公平使用。
速率限制的类型与数值
Claude API的速率限制主要分为三种类型:
- 请求频率限制(RPM):限制每分钟可发送的请求数量
- 输入令牌限制(ITPM):限制每分钟可处理的输入令牌数
- 输出令牌限制(OTPM):限制每分钟可生成的输出令牌数
这三种限制同时存在,任何一种超出限制都会触发429错误。以下是Claude官方公布的限制数值:
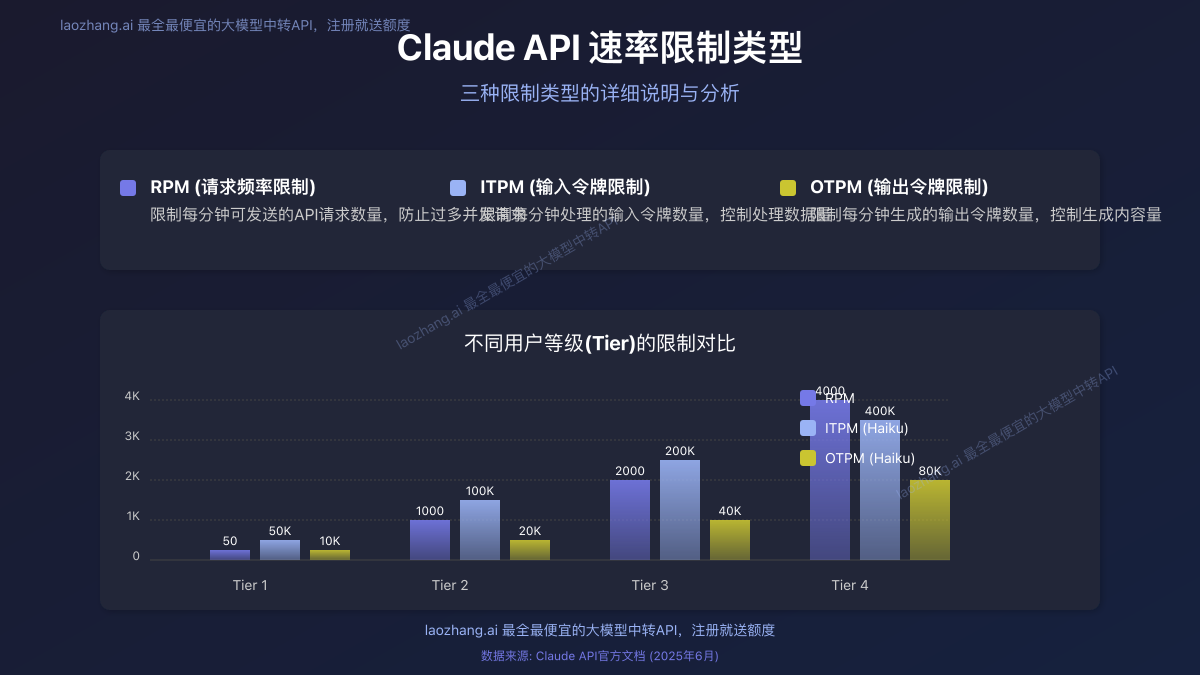
不同用户等级的限制差异
Anthropic根据用户等级(Tier)设置不同的限制标准。用户等级从Tier 1到Tier 4,限制逐级放宽:
| 等级 | 每分钟请求数(RPM) | 每分钟输入令牌(ITPM) | 每分钟输出令牌(OTPM) | 信用要求 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | 50 | 20,000-50,000 | 4,000-10,000 | $5起 |
| Tier 2 | 1,000 | 40,000-100,000 | 8,000-20,000 | $40起 |
| Tier 3 | 2,000 | 80,000-200,000 | 16,000-40,000 | $200起 |
| Tier 4 | 4,000 | 200,000-400,000 | 80,000 | $400起 |
注意:不同模型(如Claude Opus、Sonnet、Haiku)在同一等级内也有不同的具体限制值。
429错误产生原因及识别
当你的应用超过上述任一限制时,Claude API将返回HTTP 429错误状态码,表示"请求过多"。响应中通常包含以下关键信息:
retry-after头部:建议的重试等待时间(秒)- 错误消息:指明是哪种类型的限制被触发
json{
"error": {
"type": "rate_limit_error",
"message": "You have exceeded the rate limit for input_tokens. Please slow down your requests."
}
}
理解这些限制机制后,我们可以针对性地制定解决策略。
8种专业解决方案
基于对Claude API速率限制的深入理解,我们总结了8种有效的解决方案,从最简单直接到更复杂但更强大的方法,适合不同场景和需求。
解决方案1:使用laozhang.ai中转服务
对于大多数开发者来说,最简单高效的解决方案是使用专业的API中转服务。laozhang.ai作为业内领先的大模型中转API平台,提供了绕过Claude API速率限制的完美解决方案:

优势:
- 更高的速率限制:laozhang.ai通过资源池化技术,为用户提供远高于官方的速率限制
- 价格优惠:费用低至官方7折,节省开发成本
- 零修改接入:API格式与官方完全兼容,只需更换API端点即可使用
- 多模型支持:除Claude外,还支持GPT-4、Gemini等多种模型,一个API密钥通用
- 注册即送额度:新用户注册即送测试额度,无风险体验
使用方法:
- 访问laozhang.ai注册账号
- 获取API密钥
- 将API请求从官方端点切换到laozhang.ai端点
python# 官方API调用
import anthropic
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key="your-claude-api-key")
# 替换为laozhang.ai API调用
import requests
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Bearer your-laozhang-api-key"
}
data = {
"model": "claude-3-opus-20240229",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}
response = requests.post("https://api.laozhang.ai/v1/chat/completions", headers=headers, json=data)
解决方案2:实现智能重试机制
如果你希望继续直接使用Claude官方API,最基础的解决方案是实现智能重试机制。当遇到429错误时,根据API返回的retry-after头部或使用指数退避策略进行重试:
pythonimport time
import random
import requests
def call_claude_api_with_backoff(prompt, max_retries=5):
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"x-api-key": "your-api-key",
"anthropic-version": "2023-06-01"
}
data = {
"model": "claude-3-opus-20240229",
"max_tokens": 1000,
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
}
retries = 0
while retries <= max_retries:
try:
response = requests.post(
"https://api.anthropic.com/v1/messages",
headers=headers,
json=data
)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()
if response.status_code == 429:
retry_after = int(response.headers.get("retry-after", 60))
# 添加随机抖动避免同步效应
wait_time = retry_after + random.uniform(0, 5)
print(f"Rate limited. Waiting {wait_time:.2f} seconds...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
retries += 1
else:
response.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
# 指数退避
wait_time = (2 ** retries) + random.uniform(0, 1)
print(f"Retrying in {wait_time:.2f} seconds...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
retries += 1
raise Exception("Maximum retries exceeded")
这种方法简单有效,适合请求量不大且不急需实时响应的场景。
解决方案3:请求队列与节流控制
对于需要更精确控制请求速率的场景,可以实现请求队列和节流控制机制:
pythonimport time
import threading
import queue
class ClaudeAPIThrottler:
def __init__(self, rpm_limit=45): # 设置略低于实际限制
self.queue = queue.Queue()
self.rpm_limit = rpm_limit
self.interval = 60.0 / rpm_limit # 请求间隔时间
self.last_request_time = 0
self.lock = threading.Lock()
# 启动处理线程
self.worker_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._process_queue, daemon=True)
self.worker_thread.start()
def add_request(self, callback, *args, **kwargs):
"""添加API请求到队列"""
self.queue.put((callback, args, kwargs))
def _process_queue(self):
"""处理队列中的请求,确保不超过速率限制"""
while True:
callback, args, kwargs = self.queue.get()
with self.lock:
# 计算需要等待的时间
current_time = time.time()
time_since_last = current_time - self.last_request_time
wait_time = max(0, self.interval - time_since_last)
if wait_time > 0:
time.sleep(wait_time)
# 执行请求
try:
result = callback(*args, **kwargs)
# 可以添加结果回调处理
except Exception as e:
print(f"Request failed: {e}")
self.last_request_time = time.time()
self.queue.task_done()
# 使用示例
throttler = ClaudeAPIThrottler(rpm_limit=45)
def make_claude_request(prompt):
# 实际的API调用函数
# ...
# 添加请求到队列
for prompt in prompts:
throttler.add_request(make_claude_request, prompt)
这种方法在客户端主动控制请求速率,避免触发429错误,适合需要处理大量请求的应用。
解决方案4:批处理请求
Claude API支持批量处理功能,可以通过一次请求处理多个输入,从而更有效地利用速率限制配额:
pythonimport anthropic
def batch_process_requests(prompts, batch_size=10):
"""批量处理多个提示"""
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key="your-api-key")
results = []
# 将提示分批处理
for i in range(0, len(prompts), batch_size):
batch = prompts[i:i+batch_size]
batch_messages = []
for prompt in batch:
batch_messages.append({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
"max_tokens": 500
})
try:
response = client.batch.create(
requests=batch_messages,
model="claude-3-haiku-20240307"
)
for completion in response.completions:
results.append(completion.message.content)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing batch: {e}")
return results
批处理方法可以显著减少API调用次数,适合非实时处理大量数据的场景。
解决方案5:模型选择与参数优化
通过优化模型选择和请求参数,可以在不改变代码架构的情况下减轻速率限制的影响:
模型选择优化:
- 对于简单任务使用Claude Haiku,它有更宽松的速率限制
- 只在必要时使用Claude Opus等高级模型
参数优化:
- 减少输入令牌:精简提示词,移除不必要的上下文
- 限制输出令牌:设置合理的
max_tokens值 - 使用系统提示:添加系统提示引导模型生成简洁回复
python# 优化前
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-opus-20240229",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "请详细描述人工智能的历史和发展..."}],
max_tokens=4000
)
# 优化后
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-haiku-20240307", # 使用更轻量级的模型
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "请提供简洁明了的回答"},
{"role": "user", "content": "简述AI发展关键里程碑"}
],
max_tokens=500 # 限制输出长度
)
解决方案6:多账户轮询
对于需要高并发处理的应用,可以使用多个Claude API账户轮流处理请求:
pythonimport random
class ClaudeAPILoadBalancer:
def __init__(self, api_keys):
self.api_keys = api_keys
self.clients = [anthropic.Anthropic(api_key=key) for key in api_keys]
self.current_index = 0
def get_client(self, strategy="round_robin"):
"""获取API客户端,支持多种负载均衡策略"""
if strategy == "round_robin":
client = self.clients[self.current_index]
self.current_index = (self.current_index + 1) % len(self.clients)
return client
elif strategy == "random":
return random.choice(self.clients)
else:
raise ValueError("不支持的负载均衡策略")
def call_api(self, prompt, model="claude-3-sonnet-20240229", strategy="round_robin"):
"""调用API并自动负载均衡"""
client = self.get_client(strategy)
try:
response = client.messages.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
return response
except Exception as e:
print(f"API调用失败: {e}")
# 可以添加故障转移逻辑
return None
# 使用示例
api_keys = ["key1", "key2", "key3"]
balancer = ClaudeAPILoadBalancer(api_keys)
# 调用API
response = balancer.call_api("你好,Claude!", strategy="random")
多账户轮询可以线性提升可处理的请求量,但需要管理多个API密钥和账单。
解决方案7:缓存与本地模型结合
对于重复性高的请求,实现缓存机制可以显著减少API调用次数:
pythonimport hashlib
import json
import redis
class ClaudeAPICache:
def __init__(self, redis_url="redis://localhost:6379/0", ttl=3600):
self.redis = redis.from_url(redis_url)
self.ttl = ttl # 缓存有效期(秒)
def _generate_key(self, model, messages):
"""生成缓存键"""
key_data = {
"model": model,
"messages": messages
}
key_string = json.dumps(key_data, sort_keys=True)
return f"claude_cache:{hashlib.md5(key_string.encode()).hexdigest()}"
def get_cached_response(self, model, messages):
"""获取缓存的响应"""
cache_key = self._generate_key(model, messages)
cached = self.redis.get(cache_key)
if cached:
return json.loads(cached)
return None
def cache_response(self, model, messages, response):
"""缓存API响应"""
cache_key = self._generate_key(model, messages)
self.redis.setex(
cache_key,
self.ttl,
json.dumps(response)
)
def call_api_with_cache(self, client, model, messages):
"""调用API并使用缓存"""
cached = self.get_cached_response(model, messages)
if cached:
return cached
# 缓存未命中,调用API
response = client.messages.create(
model=model,
messages=messages
)
# 缓存响应
response_dict = response.model_dump()
self.cache_response(model, messages, response_dict)
return response
此外,可以结合本地小型模型处理简单查询,只将复杂任务发送给Claude API,进一步减少API调用。
解决方案8:升级服务等级
如果你的应用需要大量处理能力,升级Claude API账户等级是一个直接的解决方案:
- Tier 2:存入$40,RPM提升至1,000
- Tier 3:存入$200,RPM提升至2,000
- Tier 4:存入$400,RPM提升至4,000
- 企业级:联系Anthropic销售团队,获取定制限制
升级账户等级虽然增加了成本,但对于商业应用来说,获得稳定可靠的服务能力往往是值得的投资。
代码示例与最佳实践
以下是一个综合了多种解决方案的完整示例,包括重试、节流、缓存和错误处理:
pythonimport time
import random
import redis
import hashlib
import json
import requests
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional
@dataclass
class ClaudeConfig:
api_key: str
model: str = "claude-3-sonnet-20240229"
api_base: str = "https://api.anthropic.com/v1"
rpm_limit: int = 45
cache_ttl: int = 3600 # 缓存有效期(秒)
max_retries: int = 3
class ClaudeClient:
def __init__(self, config: ClaudeConfig, redis_url: Optional[str] = None):
self.config = config
self.last_request_time = 0
self.request_interval = 60.0 / config.rpm_limit
# 初始化Redis缓存(如果提供)
self.redis = redis.from_url(redis_url) if redis_url else None
def _wait_for_rate_limit(self):
"""等待适当时间以符合速率限制"""
current_time = time.time()
time_since_last = current_time - self.last_request_time
wait_time = max(0, self.request_interval - time_since_last)
if wait_time > 0:
time.sleep(wait_time)
def _generate_cache_key(self, messages: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> str:
"""生成缓存键"""
if not self.redis:
return ""
key_data = {
"model": self.config.model,
"messages": messages
}
key_string = json.dumps(key_data, sort_keys=True)
return f"claude_cache:{hashlib.md5(key_string.encode()).hexdigest()}"
def _get_cached_response(self, messages: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""获取缓存的响应"""
if not self.redis:
return None
cache_key = self._generate_cache_key(messages)
cached = self.redis.get(cache_key)
if cached:
return json.loads(cached)
return None
def _cache_response(self, messages: List[Dict[str, Any]], response: Dict):
"""缓存API响应"""
if not self.redis:
return
cache_key = self._generate_cache_key(messages)
self.redis.setex(
cache_key,
self.config.cache_ttl,
json.dumps(response)
)
def call(self, messages: List[Dict[str, Any]], max_tokens: int = 1000) -> Dict:
"""调用Claude API,包含重试、节流和缓存机制"""
# 检查缓存
cached = self._get_cached_response(messages)
if cached:
return cached
# 应用速率限制
self._wait_for_rate_limit()
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"x-api-key": self.config.api_key,
"anthropic-version": "2023-06-01"
}
data = {
"model": self.config.model,
"max_tokens": max_tokens,
"messages": messages
}
retries = 0
while retries <= self.config.max_retries:
try:
response = requests.post(
f"{self.config.api_base}/messages",
headers=headers,
json=data
)
self.last_request_time = time.time()
if response.status_code == 200:
result = response.json()
# 缓存结果
self._cache_response(messages, result)
return result
if response.status_code == 429:
retry_after = int(response.headers.get("retry-after", 60))
# 添加随机抖动
wait_time = retry_after + random.uniform(0, 5)
print(f"速率限制触发,等待 {wait_time:.2f} 秒...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
retries += 1
continue
# 其他错误
response.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求错误: {e}")
# 指数退避重试
wait_time = (2 ** retries) + random.uniform(0, 1)
print(f"{wait_time:.2f} 秒后重试...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
retries += 1
raise Exception("超过最大重试次数")
# 使用示例
config = ClaudeConfig(
api_key="your-api-key",
model="claude-3-haiku-20240307",
rpm_limit=45
)
client = ClaudeClient(config, redis_url="redis://localhost:6379/0")
try:
response = client.call([
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude!"}
])
print(response["content"][0]["text"])
except Exception as e:
print(f"调用失败: {e}")
常见问题解答
Q1: 我应该选择哪种解决方案?
A1: 这取决于你的具体需求:
- 对于简单项目或快速开发:使用laozhang.ai中转服务最方便
- 对于中小规模应用:实现重试机制和请求队列
- 对于大规模商业应用:考虑多账户轮询或升级服务等级
Q2: laozhang.ai中转服务是否稳定可靠?
A2: laozhang.ai作为专业的API中转服务,采用多节点部署和负载均衡技术,提供99.9%的可用性保证。与直接使用官方API相比,它不仅解决了速率限制问题,还提供了更优惠的价格和更丰富的功能。
Q3: 使用中转服务会影响响应速度吗?
A3: 高质量的中转服务如laozhang.ai通常不会明显影响响应速度。在某些地区,由于网络优化,中转服务的响应速度可能甚至优于直接调用官方API。
Q4: 我的应用需要处理突发流量,应该如何设计?
A4: 对于需要处理突发流量的应用,建议采用以下组合策略:
- 实现请求队列系统,平滑处理突发请求
- 使用缓存机制,减少重复请求
- 考虑使用laozhang.ai等中转服务提升处理能力
- 实现降级策略,在极端负载情况下使用本地模型或简化响应
Q5: 如何监控API使用情况和速率限制状态?
A5: 可以通过以下方式监控API使用情况:
- 记录所有API请求和响应
- 监控429错误的频率和时间分布
- 跟踪每分钟请求数、输入令牌和输出令牌数量
- 使用Anthropic Console中的使用统计功能
- 如使用laozhang.ai,可通过其管理面板查看详细使用统计
Q6: 使用批处理API有什么注意事项?
A6: 使用批处理API时需注意:
- 每个批处理请求仍计入RPM限制
- 批处理中的所有输入令牌总和计入ITPM限制
- 批处理请求的最大大小有限制
- 批处理适合相似的任务,不同类型的任务可能需要分开处理
总结与建议
Claude API的速率限制是开发者必须面对的挑战,但通过本文提供的8种解决方案,你可以有效地突破这些限制,构建更强大、更可靠的AI应用。
根据我们的经验,最理想的解决方案通常是组合多种策略:
- 基础层面:优化提示词和模型选择,减少不必要的令牌消耗
- 技术层面:实现智能重试、请求队列和缓存机制
- 资源层面:对于商业应用,考虑使用laozhang.ai中转服务或升级Claude API账户等级
无论你是个人开发者还是企业团队,选择适合自己需求的解决方案,可以有效地平衡性能、成本和开发复杂度,让你的AI应用更上一层楼。
🎯 开始行动:访问laozhang.ai注册账户,获取免费额度,体验无速率限制的Claude API使用体验!
希望这篇文章能帮助你解决Claude API速率限制的问题。如果你有任何问题或需要进一步的技术支持,请在评论区留言,我们会尽快回复。
更新日志:
- 2025.06.15:首次发布
- 2025.06.15:更新最新速率限制数据
