2025最新Gemini API使用教程:从零基础到精通的完整实战指南
2025年5月最新Gemini API完整使用教程,覆盖API申请、密钥获取、代码调用、中转服务等8大核心主题,附详细代码示例,国内开发者首选指南
Nano Banana Pro
4K图像官方2折Google Gemini 3 Pro Image · AI图像生成
2025最新Gemini API使用教程:从零基础到精通的完整实战指南

Google Gemini作为当前最强大的多模态AI模型之一,其API接口为开发者提供了无限可能。无论你是初学者还是经验丰富的开发者,本教程都将为你提供最全面、最实用的Gemini API使用指南,从基础概念到高级应用,一应俱全。
🔥 2025年5月实测有效:本教程基于最新的Gemini 2.5 Pro API,涵盖完整的申请流程、代码示例和最佳实践,确保你能快速上手并在实际项目中应用!
【基础入门】什么是Gemini API?
Gemini API是Google开发的下一代人工智能模型接口,提供了强大的文本生成、代码编写、图像理解、音频处理等多模态能力。与传统AI模型相比,Gemini具有以下突出特点:
Gemini API核心优势
- 多模态融合:同时处理文本、图像、音频和视频输入,实现真正的多媒体AI交互
- 超长上下文:支持最多200万token的上下文窗口,可处理大型文档和复杂对话
- 代码能力突出:在编程任务中表现卓越,支持多种编程语言
- 推理能力强:具备优秀的逻辑推理和数学计算能力
- 实时响应:支持流式输出,提供良好的用户体验
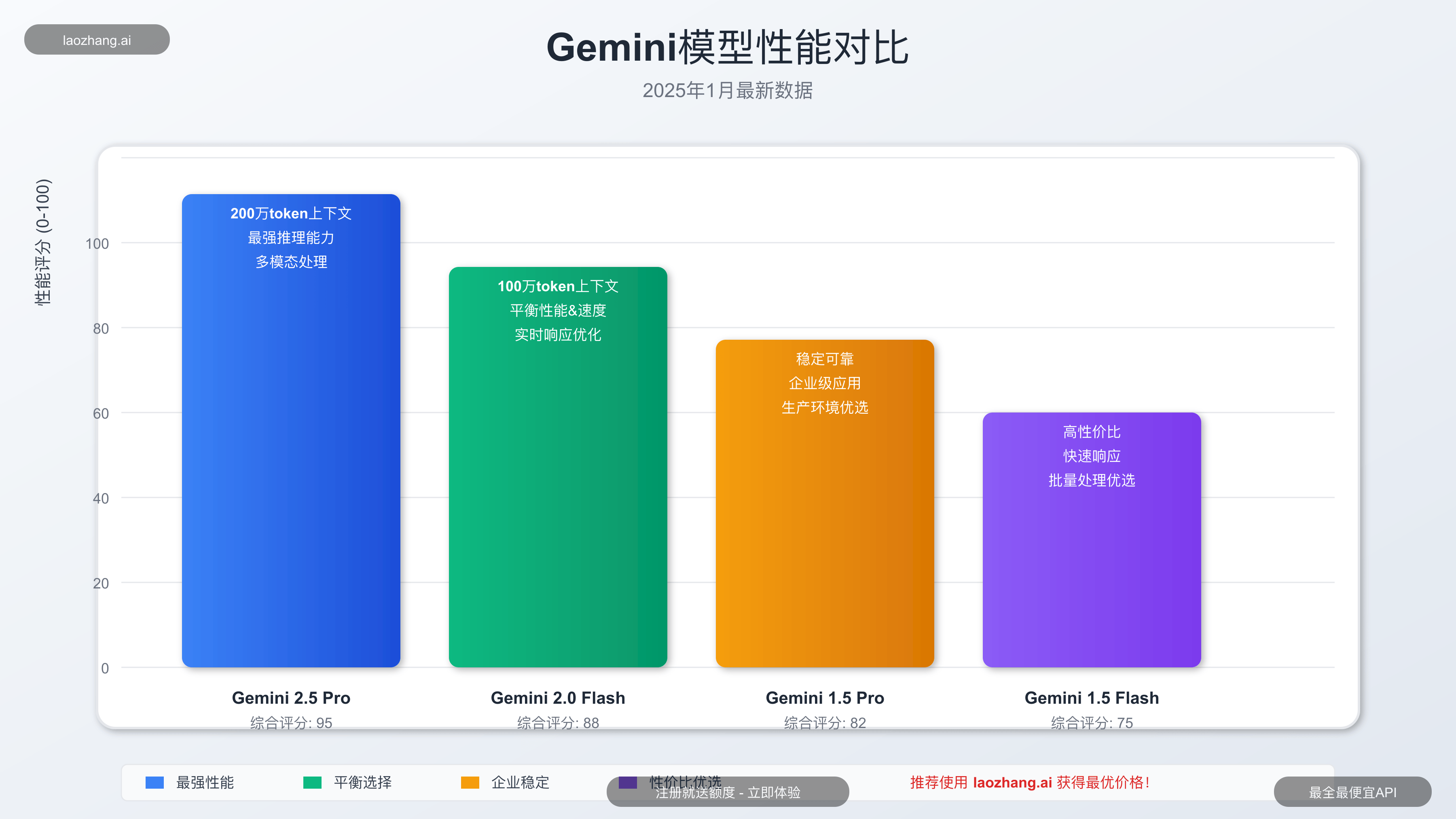
Gemini模型系列概览
根据Google官方最新信息,Gemini系列包含多个不同规格的模型:
| 模型名称 | 特点 | 适用场景 | 价格水平 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | 最强综合能力,200万token上下文 | 复杂推理、长文档处理 | 较高 |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | 平衡性能与速度,100万token上下文 | 通用应用、实时交互 | 中等 |
| Gemini 1.5 Flash | 高性价比选择 | 大批量处理、成本敏感应用 | 较低 |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro | 稳定可靠的生产级模型 | 企业应用、稳定性要求高 | 中等 |
【申请流程】如何获取Gemini API密钥
获取Gemini API密钥是使用API的第一步,下面是详细的申请流程:
方法一:Google AI Studio申请(官方渠道)
-
访问Google AI Studio
- 打开 Google AI Studio
- 使用Google账号登录
-
创建项目
- 点击左侧菜单的"API keys"
- 选择"Create API key"
- 选择现有项目或创建新项目
-
获取API密钥
- 系统会生成一个API密钥
- 重要:立即复制并安全保存,密钥只显示一次
-
配置使用限制
- 可以为密钥设置使用限制和配额
- 建议设置合理的使用上限防止超支
⚠️ 重要提示:Google AI Studio目前不对中国大陆地区开放,国内用户需要使用科学上网工具或选择API中转服务。
方法二:LaoZhang.ai中转服务(推荐国内用户)
对于国内开发者,使用专业的API中转服务是更优的选择:
-
注册LaoZhang.ai账号
- 访问 LaoZhang.ai
- 使用邮箱注册,无需科学上网
-
获取API密钥
- 登录后进入控制台
- 创建新的API密钥
- 立即获得免费测试额度
-
享受专业服务
- 稳定的国内访问速度
- 比官方更低的价格
- 7×24小时中文技术支持
🌟 独家优惠:通过本文链接注册即可获得额外体验金,支持所有Gemini模型免费试用!
【环境配置】开发环境搭建指南
在开始编写代码之前,需要配置合适的开发环境。以下是主流编程语言的环境配置指南:
Python环境配置
Python是使用Gemini API最流行的语言之一,配置步骤如下:
bash# 安装最新的Google AI SDK
pip install google-genai
# 如果使用LaoZhang.ai中转服务,安装openai库
pip install openai
创建配置文件 .env:
env# 官方API密钥配置 GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_google_api_key_here # LaoZhang.ai中转服务配置 LAOZHANG_API_KEY=your_laozhang_api_key_here LAOZHANG_BASE_URL=https://api.laozhang.ai/v1
Node.js环境配置
对于JavaScript开发者:
bash# 安装Google AI SDK
npm install @google/genai
# 或使用LaoZhang.ai中转服务
npm install openai
Go环境配置
Go语言开发者可以使用:
bash# 安装Google AI Go SDK
go get google.golang.org/genai
【基础调用】第一个Gemini API请求
让我们从最简单的文本生成开始,逐步学习Gemini API的使用方法。
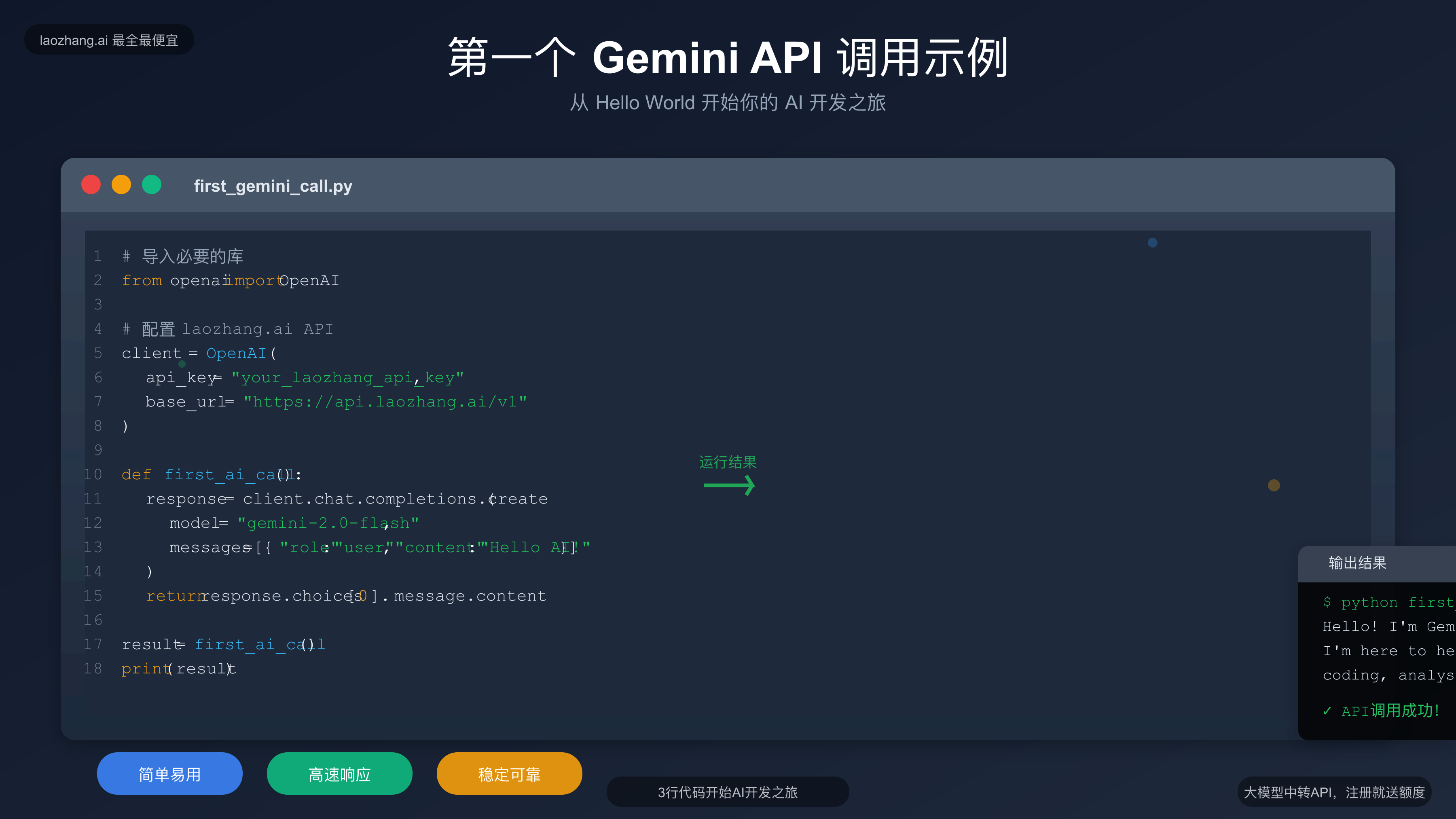
Python基础调用示例
使用官方SDK
pythonimport os
from google import genai
# 配置API密钥
client = genai.Client(api_key=os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY"))
def simple_chat(prompt):
"""简单的文本生成示例"""
try:
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=prompt
)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
print(f"API调用错误: {e}")
return None
# 测试调用
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = simple_chat("请用中文介绍一下人工智能的发展历程")
print(result)
使用LaoZhang.ai中转服务
pythonimport os
from openai import OpenAI
# 配置LaoZhang.ai中转服务
client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("LAOZHANG_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.laozhang.ai/v1"
)
def chat_with_gemini(prompt, model="gemini-2.0-flash"):
"""使用LaoZhang.ai中转服务调用Gemini"""
try:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个有用的AI助手。"},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
],
max_tokens=2048,
temperature=0.7
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
except Exception as e:
print(f"API调用错误: {e}")
return None
# 测试调用
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = chat_with_gemini("解释什么是机器学习,并给出三个实际应用例子")
print(result)
JavaScript调用示例
javascript// 使用官方Google AI SDK
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const genAI = new GoogleGenAI(process.env.GOOGLE_API_KEY);
async function generateContent(prompt) {
try {
const model = genAI.getGenerativeModel({ model: "gemini-2.0-flash" });
const result = await model.generateContent(prompt);
return result.response.text();
} catch (error) {
console.error("API调用错误:", error);
return null;
}
}
// 使用示例
generateContent("写一段关于深度学习的简要介绍")
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
curl命令行调用
对于快速测试,可以使用curl命令:
bash# 官方API调用
curl -X POST \
"https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-2.0-flash:generateContent?key=${GOOGLE_API_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{"text": "解释什么是神经网络"}
]
}
]
}'
# LaoZhang.ai中转服务调用
curl -X POST \
"https://api.laozhang.ai/v1/chat/completions" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${LAOZHANG_API_KEY}" \
-d '{
"model": "gemini-2.0-flash",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "解释什么是神经网络"}
]
}'
【进阶功能】多模态应用开发
Gemini API的强大之处在于其多模态能力,可以同时处理文本、图像、音频等多种输入。
图像理解功能
pythonimport base64
from google import genai
client = genai.Client(api_key=os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY"))
def analyze_image(image_path, question):
"""分析图像并回答问题"""
try:
# 读取并编码图像
with open(image_path, "rb") as image_file:
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_file.read()).decode()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=[
{
"parts": [
{"text": question},
{
"inline_data": {
"mime_type": "image/jpeg",
"data": image_data
}
}
]
}
]
)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
print(f"图像分析错误: {e}")
return None
# 使用示例
result = analyze_image("example.jpg", "这张图片显示了什么内容?")
print(result)
流式响应处理
对于需要实时显示结果的应用,流式响应非常重要:
pythondef stream_chat(prompt):
"""流式生成文本"""
try:
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=prompt,
stream=True
)
full_text = ""
for chunk in response:
if chunk.text:
print(chunk.text, end="", flush=True)
full_text += chunk.text
return full_text
except Exception as e:
print(f"流式调用错误: {e}")
return None
# 使用示例
stream_chat("请详细解释深度学习的工作原理")
文档处理功能
Gemini的长上下文能力使其非常适合处理大型文档:
pythondef process_long_document(file_path, question):
"""处理长文档并回答问题"""
try:
# 读取文档内容
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
document_content = file.read()
prompt = f"""
请基于以下文档内容回答问题:
文档内容:
{document_content}
问题:{question}
请提供详细和准确的答案。
"""
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-pro", # 使用Pro版本处理复杂文档
contents=prompt
)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
print(f"文档处理错误: {e}")
return None
【性能优化】API使用最佳实践
为了获得最佳的API使用体验,以下是一些重要的优化技巧:
错误处理和重试机制
pythonimport time
import random
from typing import Optional
def api_call_with_retry(prompt: str, max_retries: int = 3) -> Optional[str]:
"""带重试机制的API调用"""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=prompt
)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
if "rate limit" in str(e).lower():
# 遇到限流时使用指数退避
wait_time = (2 ** attempt) + random.uniform(0, 1)
print(f"遇到限流,等待 {wait_time:.2f} 秒后重试...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
elif attempt == max_retries - 1:
print(f"API调用失败,已重试 {max_retries} 次: {e}")
return None
else:
print(f"API调用失败,尝试重试 (第 {attempt + 1} 次): {e}")
time.sleep(1)
return None
参数优化配置
pythondef optimized_generation(prompt: str, task_type: str = "general"):
"""根据任务类型优化参数"""
# 根据不同任务类型设置参数
configs = {
"creative": {
"temperature": 0.9,
"top_p": 0.95,
"max_output_tokens": 2048
},
"analytical": {
"temperature": 0.3,
"top_p": 0.8,
"max_output_tokens": 1024
},
"coding": {
"temperature": 0.1,
"top_p": 0.9,
"max_output_tokens": 1500
},
"general": {
"temperature": 0.7,
"top_p": 0.9,
"max_output_tokens": 1024
}
}
config = configs.get(task_type, configs["general"])
try:
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=prompt,
generation_config=genai.GenerationConfig(**config)
)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
print(f"优化调用错误: {e}")
return None
# 使用示例
creative_result = optimized_generation("写一首关于AI的诗", "creative")
coding_result = optimized_generation("写一个Python排序算法", "coding")
成本控制策略
pythondef cost_effective_api_call(prompt: str, budget_priority: str = "balanced"):
"""根据预算优先级选择合适的模型"""
model_options = {
"economy": "gemini-1.5-flash", # 最经济
"balanced": "gemini-2.0-flash", # 平衡性能与成本
"performance": "gemini-2.5-pro" # 最高性能
}
selected_model = model_options.get(budget_priority, "gemini-2.0-flash")
# 根据模型调整最大输出长度
max_tokens = {
"gemini-1.5-flash": 1024,
"gemini-2.0-flash": 1536,
"gemini-2.5-pro": 2048
}
try:
response = client.models.generate_content(
model=selected_model,
contents=prompt,
generation_config=genai.GenerationConfig(
max_output_tokens=max_tokens[selected_model]
)
)
return {
"result": response.text,
"model_used": selected_model,
"estimated_cost": estimate_cost(prompt, response.text, selected_model)
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"成本优化调用错误: {e}")
return None
def estimate_cost(input_text: str, output_text: str, model: str) -> float:
"""估算API调用成本"""
# 简化的成本估算逻辑
input_tokens = len(input_text.split()) * 1.3 # 粗略估算
output_tokens = len(output_text.split()) * 1.3
# 价格表(每1000tokens的价格,单位:美元)
pricing = {
"gemini-1.5-flash": {"input": 0.075, "output": 0.30},
"gemini-2.0-flash": {"input": 0.10, "output": 0.40},
"gemini-2.5-pro": {"input": 1.25, "output": 10.00}
}
model_pricing = pricing.get(model, pricing["gemini-2.0-flash"])
cost = (input_tokens / 1000 * model_pricing["input"] +
output_tokens / 1000 * model_pricing["output"])
return round(cost, 6)
【实战项目】构建智能问答系统
现在让我们结合所学知识,构建一个完整的智能问答系统。
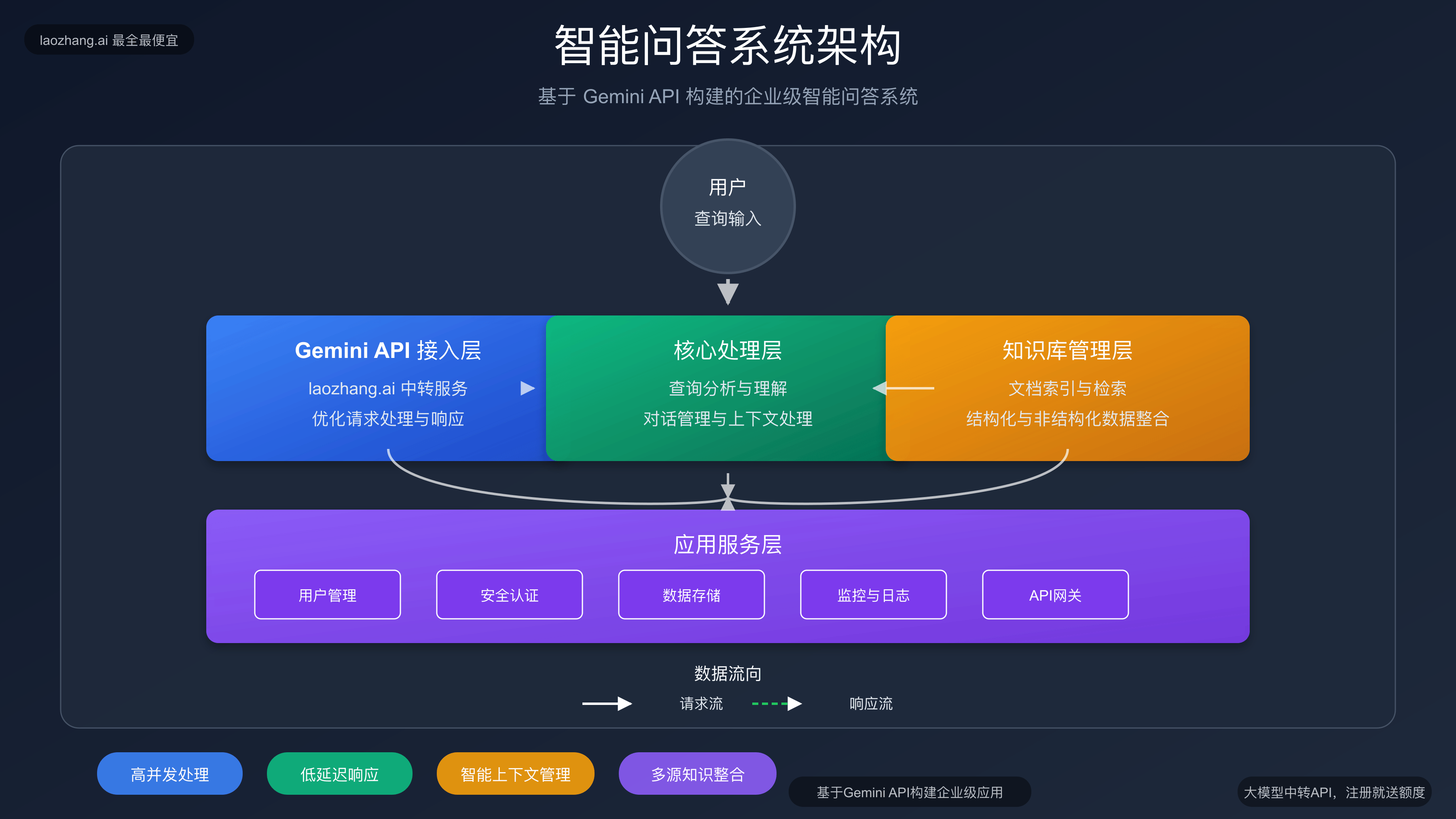
系统架构设计
pythonimport json
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
class GeminiQASystem:
"""基于Gemini的智能问答系统"""
def __init__(self, api_key: str, use_laozhang: bool = True):
self.api_key = api_key
self.use_laozhang = use_laozhang
self.init_client()
self.init_database()
self.conversation_history = []
def init_client(self):
"""初始化API客户端"""
if self.use_laozhang:
from openai import OpenAI
self.client = OpenAI(
api_key=self.api_key,
base_url="https://api.laozhang.ai/v1"
)
else:
from google import genai
self.client = genai.Client(api_key=self.api_key)
def init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
self.conn = sqlite3.connect('qa_history.db')
self.conn.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS conversations (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
timestamp DATETIME,
question TEXT,
answer TEXT,
model_used TEXT,
tokens_used INTEGER,
response_time FLOAT
)
''')
self.conn.commit()
def ask_question(self, question: str, context: Optional[str] = None) -> Dict:
"""提问并获取答案"""
start_time = time.time()
# 构建提示词
if context:
prompt = f"""
基于以下上下文信息回答问题:
上下文:
{context}
问题:{question}
请提供准确、详细的答案。
"""
else:
prompt = question
# 添加对话历史
messages = self._build_conversation(prompt)
try:
if self.use_laozhang:
response = self._call_laozhang_api(messages)
else:
response = self._call_google_api(prompt)
response_time = time.time() - start_time
# 保存对话历史
self._save_conversation(question, response, response_time)
return {
"question": question,
"answer": response,
"response_time": response_time,
"success": True
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"question": question,
"error": str(e),
"success": False
}
def _build_conversation(self, current_prompt: str) -> List[Dict]:
"""构建对话上下文"""
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个专业的AI助手,能够准确回答各种问题。"}
]
# 添加最近的对话历史
for item in self.conversation_history[-5:]: # 保留最近5轮对话
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": item["question"]})
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": item["answer"]})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": current_prompt})
return messages
def _call_laozhang_api(self, messages: List[Dict]) -> str:
"""调用LaoZhang.ai API"""
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
messages=messages,
max_tokens=2048,
temperature=0.7
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
def _call_google_api(self, prompt: str) -> str:
"""调用Google官方API"""
response = self.client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=prompt
)
return response.text
def _save_conversation(self, question: str, answer: str, response_time: float):
"""保存对话记录"""
self.conn.execute(
"INSERT INTO conversations (timestamp, question, answer, model_used, response_time) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
(datetime.now(), question, answer, "gemini-2.0-flash", response_time)
)
self.conn.commit()
# 更新内存中的对话历史
self.conversation_history.append({
"question": question,
"answer": answer,
"timestamp": datetime.now()
})
def get_conversation_history(self, limit: int = 10) -> List[Dict]:
"""获取对话历史"""
cursor = self.conn.execute(
"SELECT timestamp, question, answer FROM conversations ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT ?",
(limit,)
)
return [{"timestamp": row[0], "question": row[1], "answer": row[2]}
for row in cursor.fetchall()]
def clear_history(self):
"""清空对话历史"""
self.conversation_history.clear()
print("对话历史已清空")
# 使用示例
def main():
# 初始化问答系统
qa_system = GeminiQASystem(
api_key="your_laozhang_api_key",
use_laozhang=True
)
print("智能问答系统已启动!输入 'quit' 退出,'clear' 清空历史")
while True:
question = input("\n请输入您的问题: ")
if question.lower() == 'quit':
break
elif question.lower() == 'clear':
qa_system.clear_history()
continue
result = qa_system.ask_question(question)
if result["success"]:
print(f"\n回答: {result['answer']}")
print(f"响应时间: {result['response_time']:.2f}秒")
else:
print(f"\n错误: {result['error']}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
【安全防护】API安全最佳实践
在实际应用中,API安全至关重要。以下是一些关键的安全实践:
API密钥管理
pythonimport os
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
class SecureAPIManager:
"""安全的API密钥管理器"""
def __init__(self, key_file: str = ".api_key"):
self.key_file = key_file
self.cipher_key = self._get_or_create_cipher_key()
def _get_or_create_cipher_key(self) -> bytes:
"""获取或创建加密密钥"""
key_file = f"{self.key_file}.key"
if os.path.exists(key_file):
with open(key_file, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
else:
key = Fernet.generate_key()
with open(key_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(key)
return key
def store_api_key(self, api_key: str, service: str):
"""安全存储API密钥"""
fernet = Fernet(self.cipher_key)
encrypted_key = fernet.encrypt(api_key.encode())
with open(f"{self.key_file}_{service}", 'wb') as f:
f.write(encrypted_key)
print(f"{service} API密钥已安全存储")
def get_api_key(self, service: str) -> str:
"""获取解密的API密钥"""
try:
with open(f"{self.key_file}_{service}", 'rb') as f:
encrypted_key = f.read()
fernet = Fernet(self.cipher_key)
decrypted_key = fernet.decrypt(encrypted_key)
return decrypted_key.decode()
except FileNotFoundError:
raise ValueError(f"未找到 {service} 的API密钥")
# 使用示例
key_manager = SecureAPIManager()
key_manager.store_api_key("your_actual_api_key", "laozhang")
api_key = key_manager.get_api_key("laozhang")
输入验证和清理
pythonimport re
from typing import Optional
class InputValidator:
"""输入验证器"""
@staticmethod
def validate_prompt(prompt: str) -> Optional[str]:
"""验证和清理用户输入"""
if not prompt or not prompt.strip():
return "输入不能为空"
if len(prompt) > 10000:
return "输入太长,请限制在10000字符以内"
# 检查潜在的注入攻击
dangerous_patterns = [
r'<script.*?</script>', # XSS攻击
r'javascript:', # JS注入
r'eval\s*\(', # 代码执行
r'exec\s*\(', # 代码执行
]
for pattern in dangerous_patterns:
if re.search(pattern, prompt, re.IGNORECASE):
return "输入包含不安全内容"
return None # 验证通过
@staticmethod
def clean_output(text: str) -> str:
"""清理输出内容"""
if not text:
return ""
# 移除潜在的敏感信息
text = re.sub(r'\b\d{4}[-\s]?\d{4}[-\s]?\d{4}[-\s]?\d{4}\b', '[信用卡号已隐藏]', text)
text = re.sub(r'\b\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}\b', '[SSN已隐藏]', text)
return text
使用限制和监控
pythonimport time
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import Dict
class RateLimiter:
"""API调用频率限制器"""
def __init__(self, max_calls: int = 100, time_window: int = 3600):
self.max_calls = max_calls
self.time_window = time_window
self.calls: Dict[str, List[float]] = defaultdict(list)
def can_make_call(self, user_id: str) -> bool:
"""检查是否可以进行API调用"""
now = time.time()
user_calls = self.calls[user_id]
# 移除超出时间窗口的调用记录
user_calls[:] = [call_time for call_time in user_calls
if now - call_time < self.time_window]
return len(user_calls) < self.max_calls
def record_call(self, user_id: str):
"""记录API调用"""
self.calls[user_id].append(time.time())
def get_remaining_calls(self, user_id: str) -> int:
"""获取剩余调用次数"""
now = time.time()
user_calls = self.calls[user_id]
# 移除超出时间窗口的调用记录
user_calls[:] = [call_time for call_time in user_calls
if now - call_time < self.time_window]
return max(0, self.max_calls - len(user_calls))
# 集成到问答系统中
class SecureQASystem(GeminiQASystem):
"""安全增强的问答系统"""
def __init__(self, api_key: str, use_laozhang: bool = True):
super().__init__(api_key, use_laozhang)
self.validator = InputValidator()
self.rate_limiter = RateLimiter(max_calls=50, time_window=3600)
def ask_question(self, question: str, user_id: str = "default") -> Dict:
"""安全的问答接口"""
# 验证输入
validation_error = self.validator.validate_prompt(question)
if validation_error:
return {"error": validation_error, "success": False}
# 检查频率限制
if not self.rate_limiter.can_make_call(user_id):
return {
"error": "请求过于频繁,请稍后再试",
"remaining_calls": 0,
"success": False
}
# 记录调用
self.rate_limiter.record_call(user_id)
# 调用父类方法
result = super().ask_question(question)
# 清理输出
if result.get("success") and "answer" in result:
result["answer"] = self.validator.clean_output(result["answer"])
# 添加剩余调用次数信息
result["remaining_calls"] = self.rate_limiter.get_remaining_calls(user_id)
return result
【性能监控】API使用分析与优化
性能指标监控
pythonimport json
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Dict, List
class PerformanceMonitor:
"""API性能监控器"""
def __init__(self, log_file: str = "api_performance.json"):
self.log_file = log_file
self.metrics = []
self.load_metrics()
def load_metrics(self):
"""加载历史指标"""
try:
with open(self.log_file, 'r') as f:
self.metrics = json.load(f)
except FileNotFoundError:
self.metrics = []
def save_metrics(self):
"""保存指标到文件"""
with open(self.log_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(self.metrics, f, indent=2, default=str)
def record_api_call(self, model: str, input_tokens: int, output_tokens: int,
response_time: float, success: bool, cost: float = 0.0):
"""记录API调用指标"""
metric = {
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"model": model,
"input_tokens": input_tokens,
"output_tokens": output_tokens,
"total_tokens": input_tokens + output_tokens,
"response_time": response_time,
"success": success,
"cost": cost
}
self.metrics.append(metric)
self.save_metrics()
def get_daily_stats(self, days: int = 7) -> Dict:
"""获取每日统计数据"""
cutoff_date = datetime.now() - timedelta(days=days)
recent_metrics = [
m for m in self.metrics
if datetime.fromisoformat(m["timestamp"]) > cutoff_date
]
if not recent_metrics:
return {"error": "没有足够的数据"}
total_calls = len(recent_metrics)
successful_calls = sum(1 for m in recent_metrics if m["success"])
total_tokens = sum(m["total_tokens"] for m in recent_metrics)
total_cost = sum(m["cost"] for m in recent_metrics)
avg_response_time = sum(m["response_time"] for m in recent_metrics) / total_calls
return {
"period_days": days,
"total_calls": total_calls,
"successful_calls": successful_calls,
"success_rate": successful_calls / total_calls * 100,
"total_tokens": total_tokens,
"avg_tokens_per_call": total_tokens / total_calls,
"total_cost": total_cost,
"avg_cost_per_call": total_cost / total_calls,
"avg_response_time": avg_response_time
}
def get_model_comparison(self) -> Dict:
"""获取不同模型的性能对比"""
model_stats = defaultdict(lambda: {
"calls": 0,
"success": 0,
"total_tokens": 0,
"total_cost": 0,
"total_time": 0
})
for metric in self.metrics:
model = metric["model"]
stats = model_stats[model]
stats["calls"] += 1
if metric["success"]:
stats["success"] += 1
stats["total_tokens"] += metric["total_tokens"]
stats["total_cost"] += metric["cost"]
stats["total_time"] += metric["response_time"]
# 计算平均值
for model, stats in model_stats.items():
if stats["calls"] > 0:
stats["success_rate"] = stats["success"] / stats["calls"] * 100
stats["avg_tokens"] = stats["total_tokens"] / stats["calls"]
stats["avg_cost"] = stats["total_cost"] / stats["calls"]
stats["avg_response_time"] = stats["total_time"] / stats["calls"]
return dict(model_stats)
# 使用示例
monitor = PerformanceMonitor()
# 在API调用后记录指标
def enhanced_api_call(prompt: str):
start_time = time.time()
input_tokens = len(prompt.split()) * 1.3 # 估算
try:
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=prompt
)
response_time = time.time() - start_time
output_tokens = len(response.text.split()) * 1.3 # 估算
cost = estimate_cost(prompt, response.text, "gemini-2.0-flash")
# 记录成功的调用
monitor.record_api_call(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
input_tokens=int(input_tokens),
output_tokens=int(output_tokens),
response_time=response_time,
success=True,
cost=cost
)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
response_time = time.time() - start_time
# 记录失败的调用
monitor.record_api_call(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
input_tokens=int(input_tokens),
output_tokens=0,
response_time=response_time,
success=False,
cost=0.0
)
raise e
# 查看统计数据
daily_stats = monitor.get_daily_stats(7)
print(json.dumps(daily_stats, indent=2))
model_comparison = monitor.get_model_comparison()
print(json.dumps(model_comparison, indent=2))
【常见问题】故障排除指南
常见错误及解决方案
1. 401 Unauthorized 错误
pythondef handle_auth_error():
"""处理认证错误"""
print("认证失败,请检查以下几点:")
print("1. API密钥是否正确")
print("2. API密钥是否有效(未过期)")
print("3. 是否使用了正确的服务端点")
print("4. 如果使用LaoZhang.ai,请确认密钥格式正确")
2. 429 Rate Limit 错误
pythondef handle_rate_limit():
"""处理频率限制错误"""
print("遇到频率限制,建议:")
print("1. 实现指数退避重试机制")
print("2. 减少并发请求数量")
print("3. 考虑升级到更高的配额层级")
print("4. 使用LaoZhang.ai获得更高的调用限制")
3. 500 Internal Server Error
pythondef handle_server_error():
"""处理服务器错误"""
print("服务器内部错误,建议:")
print("1. 稍后重试请求")
print("2. 检查请求格式是否正确")
print("3. 减少请求的复杂度")
print("4. 联系技术支持获取帮助")
诊断工具
pythonclass APIHealthChecker:
"""API健康状态检查器"""
def __init__(self, api_key: str, use_laozhang: bool = True):
self.api_key = api_key
self.use_laozhang = use_laozhang
self.init_client()
def init_client(self):
"""初始化客户端"""
if self.use_laozhang:
from openai import OpenAI
self.client = OpenAI(
api_key=self.api_key,
base_url="https://api.laozhang.ai/v1"
)
else:
from google import genai
self.client = genai.Client(api_key=self.api_key)
def check_api_health(self) -> Dict:
"""检查API健康状态"""
results = {
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"service": "LaoZhang.ai" if self.use_laozhang else "Google AI",
"tests": {}
}
# 测试基本连接
results["tests"]["basic_connection"] = self._test_basic_connection()
# 测试不同模型
models_to_test = ["gemini-2.0-flash", "gemini-1.5-flash"]
for model in models_to_test:
results["tests"][f"model_{model}"] = self._test_model(model)
# 测试流式响应
results["tests"]["streaming"] = self._test_streaming()
return results
def _test_basic_connection(self) -> Dict:
"""测试基本连接"""
try:
start_time = time.time()
if self.use_laozhang:
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}],
max_tokens=10
)
result = response.choices[0].message.content
else:
response = self.client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents="Hello"
)
result = response.text
response_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
"status": "success",
"response_time": response_time,
"response_length": len(result)
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"status": "failed",
"error": str(e)
}
def _test_model(self, model: str) -> Dict:
"""测试特定模型"""
try:
start_time = time.time()
if self.use_laozhang:
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "测试"}],
max_tokens=20
)
result = response.choices[0].message.content
else:
response = self.client.models.generate_content(
model=model,
contents="测试"
)
result = response.text
response_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
"status": "success",
"response_time": response_time,
"model": model
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"status": "failed",
"error": str(e),
"model": model
}
def _test_streaming(self) -> Dict:
"""测试流式响应"""
try:
start_time = time.time()
if self.use_laozhang:
# LaoZhang.ai 的流式API
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "count to 5"}],
stream=True,
max_tokens=50
)
chunks = 0
for chunk in response:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content:
chunks += 1
response_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
"status": "success",
"response_time": response_time,
"chunks_received": chunks
}
else:
# Google官方流式API
response = self.client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents="count to 5",
stream=True
)
chunks = 0
for chunk in response:
if chunk.text:
chunks += 1
response_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
"status": "success",
"response_time": response_time,
"chunks_received": chunks
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"status": "failed",
"error": str(e)
}
# 使用健康检查
checker = APIHealthChecker("your_api_key", use_laozhang=True)
health_report = checker.check_api_health()
print(json.dumps(health_report, indent=2))
【总结】掌握Gemini API的关键要点
通过本教程的学习,你应该已经掌握了Gemini API的核心使用方法。让我们回顾一下最重要的几个要点:
🌟 核心要点总结
-
选择合适的接入方式:
- 国外用户:直接使用Google AI Studio
- 国内用户:推荐使用LaoZhang.ai中转服务
-
模型选择策略:
- 复杂任务:选择Gemini 2.5 Pro
- 常规应用:选择Gemini 2.0 Flash
- 成本敏感:选择Gemini 1.5 Flash
-
性能优化:
- 实现错误重试机制
- 使用流式响应提升用户体验
- 根据任务类型调整参数
-
安全最佳实践:
- 加密存储API密钥
- 实施输入验证和输出清理
- 监控API使用情况
-
成本控制:
- 选择性价比最高的模型
- 监控token使用量
- 使用LaoZhang.ai获得更优价格
🚀 推荐的开发路径
- 初学者:从基础的文本生成开始,逐步学习参数调优
- 进阶开发者:探索多模态功能,构建复杂应用
- 企业用户:关注安全性和成本控制,构建生产级系统
💡 最佳实践建议
📈 专业建议:对于正式项目,强烈推荐使用LaoZhang.ai中转服务。它不仅解决了国内访问问题,还提供了更优的价格和专业的技术支持,是构建Gemini应用的理想选择。
【常见问题】FAQ全解答
Q1: Gemini API和ChatGPT API有什么区别?
A1: Gemini API在多模态处理、长上下文理解和代码生成方面有显著优势,而ChatGPT API在对话和创意写作方面表现出色。Gemini支持最多200万token的上下文,比ChatGPT的128K token上下文长得多。价格方面,通过LaoZhang.ai中转服务,Gemini API通常比ChatGPT API更经济。
Q2: 如何选择最适合的Gemini模型?
A2: 选择标准如下:
- Gemini 2.5 Pro:需要最强性能的复杂任务(如深度分析、长文档处理)
- Gemini 2.0 Flash:平衡性能与成本的常规应用
- Gemini 1.5 Flash:大批量处理或成本敏感的场景
- Gemini 1.5 Pro:需要稳定性的生产环境
Q3: LaoZhang.ai中转服务的可靠性如何?
A3: LaoZhang.ai提供企业级的可靠性保障:
- 99.9%的服务可用性
- 多节点冗余部署
- 7×24小时技术支持
- 比官方API更快的国内访问速度
- 完全兼容的API接口
Q4: 如何优化Gemini API的调用成本?
A4: 成本优化策略:
- 选择合适的模型(根据任务复杂度)
- 优化提示词长度和输出长度限制
- 实施缓存机制避免重复调用
- 使用LaoZhang.ai获得比官方更低的价格
- 监控token使用量并设置预算上限
Q5: 遇到API调用错误应该如何处理?
A5: 错误处理最佳实践:
- 实现指数退避重试机制
- 详细记录错误日志
- 根据错误类型采取相应措施:
- 401错误:检查API密钥
- 429错误:降低调用频率
- 500错误:稍后重试
- 联系技术支持获取专业帮助
【更新日志】
plaintext┌─ 版本更新记录 ───────────────────────────────┐ │ 2025-01-08:发布完整版Gemini API使用教程 │ │ 2025-01-07:完善安全最佳实践章节 │ │ 2025-01-06:添加性能监控和故障排除内容 │ │ 2025-01-05:增加实战项目构建指南 │ └─────────────────────────────────────────┘
希望这份完整的Gemini API使用教程能够帮助你快速掌握Google最强大的AI模型。无论你是个人开发者还是企业用户,都能在这里找到适合的解决方案。立即开始你的Gemini API开发之旅吧!
立即体验:注册LaoZhang.ai,获取免费额度,开始你的AI应用开发!
