How to Reduce GPT-5.2 API Cost: 8 Proven Strategies for 80% Savings [2025 Guide]
Master GPT-5.2 API cost optimization with proven strategies including prompt caching (90% discount), batch API (50% off), intelligent model routing, and semantic caching. Complete implementation guide with code examples.
Nano Banana Pro
4K图像官方2折Google Gemini 3 Pro Image · AI图像生成
The launch of GPT-5.2 in December 2025 brought unprecedented capabilities to developers worldwide, but it also introduced a pricing structure that demands careful cost management. At $1.75 per million input tokens and $14 per million output tokens, GPT-5.2 represents a 40% premium over its predecessor GPT-5. For production applications processing millions of tokens daily, these costs can quickly escalate from manageable to prohibitive without proper optimization strategies.
Understanding how to reduce GPT-5.2 API cost isn't just about cutting expenses—it's about building sustainable AI-powered applications that can scale without breaking the budget. The good news is that OpenAI has built multiple cost-saving mechanisms directly into the platform, and when combined with architectural best practices, you can achieve 50-80% cost reductions while maintaining output quality. This comprehensive guide walks you through eight proven strategies, complete with implementation details and real-world examples that demonstrate measurable savings.

Understanding GPT-5.2's Pricing Architecture
Before diving into optimization strategies, you need to understand exactly what you're paying for. GPT-5.2 comes in three distinct tiers, each designed for different use cases and budget requirements. The Instant tier handles quick daily tasks like information seeking, writing assistance, and translation work. The Thinking tier excels at complex structured work including coding, document analysis, mathematical reasoning, and multi-step planning. The Pro tier delivers maximum accuracy and reliability for the most challenging problems that demand extended reasoning capabilities.
The pricing breakdown reveals significant cost differences across these tiers. Standard GPT-5.2 charges $1.75 per million input tokens and $14 per million output tokens—roughly 40% more expensive than GPT-5's $1.25 input and $10 output pricing. However, GPT-5.2 Pro jumps dramatically to $21 per million input tokens and $168 per million output tokens, making it essential to route only truly complex queries to this tier.
| Model Variant | Input (per 1M tokens) | Output (per 1M tokens) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-5.2 Instant | $1.75 | $14.00 | Quick tasks, translation |
| GPT-5.2 Thinking | $1.75 | $14.00 | Coding, analysis |
| GPT-5.2 Pro | $21.00 | $168.00 | Complex reasoning |
| GPT-5 (baseline) | $1.25 | $10.00 | General tasks |
| GPT-5-Mini | $0.25 | $2.00 | High-volume work |
| GPT-5-Nano | $0.05 | $0.40 | Classification, tagging |
What makes this pricing structure strategically important is that output tokens cost 8x more than input tokens. This means verbose responses dramatically inflate costs compared to concise ones. A response that generates 2,000 tokens costs $0.028 in output alone, while the same information delivered in 500 tokens costs just $0.007—a 75% reduction from response optimization alone.
The 400,000-token context window in GPT-5.2 fundamentally changes how you should approach large document processing. Previous models required splitting large codebases or documentation sets across multiple API calls, each incurring its own overhead and context management complexity. With GPT-5.2's expanded context, entire technical documentation sets can now flow through a single API call, eliminating redundant context tokens that previously needed repetition across requests. Organizations processing extensive documents report 30-40% cost reductions simply from this consolidation effect.
Strategy 1: Mastering Prompt Caching for 90% Savings
OpenAI's prompt caching system represents the single most powerful cost reduction mechanism available to GPT-5.2 users, offering a staggering 90% discount on cached input tokens. This means cached tokens cost just $0.175 per million instead of the standard $1.75—effectively making repeated queries against large codebases or documentation nearly free after the initial request.
The caching system activates automatically for prompts exceeding 1,024 tokens, with the system caching in 128-token increments beyond that threshold. When a subsequent request shares the same prefix as a cached prompt, OpenAI delivers cached results with both reduced latency and dramatically lower costs. Cached prefixes typically remain active for 5-10 minutes of inactivity, extending to one hour during off-peak periods. This automatic caching operates transparently—no special configuration required on your part.
Implementing effective prompt caching requires understanding what content gets cached and how to maximize cache hit rates. The cacheable content types include message arrays containing system, user, and assistant messages; images in both linked and base64-encoded formats; tool use specifications that define function calling capabilities; and structured output schemas that constrain response formats. By organizing your prompts with common prefixes, you allow OpenAI's optimization to work most effectively.
Consider a code review system that processes multiple files from the same repository. By structuring requests with the repository context, coding standards, and review guidelines at the beginning of each prompt, followed by the specific file content at the end, you achieve cache hits on the expensive context portion while only paying full price for the variable file content. Production systems implementing this pattern report 80% cache hit rates, translating to massive cost savings on high-volume workflows.
python# Optimized prompt structure for maximum cache hits
system_prompt = """
You are a senior code reviewer for the Acme Corp repository.
Repository context: Python 3.11, FastAPI backend, React frontend
Coding standards: PEP 8, type hints required, 80% test coverage minimum
Review guidelines: Focus on security, performance, and maintainability
[Additional 1000+ tokens of context that will be cached]
"""
# This structure ensures the system prompt gets cached
# Only the file content varies between requests
def review_file(file_content: str):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt}, # Cached after first call
{"role": "user", "content": f"Review this file:\n{file_content}"} # Variable
]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
The key optimization best practices for prompt caching start with front-loading static content—place all unchanging material like system instructions, context documents, and standard guidelines at the beginning of your prompts. Use standardized templates across similar tasks to maximize the cacheable prefix portion. Batch similar requests consecutively rather than interleaving different query types, as this keeps caches warm for each query pattern. Finally, monitor the cached_tokens values in API responses to track your actual cache performance and identify optimization opportunities.
Document analysis workflows demonstrate the dramatic impact of proper caching implementation. A system that previously cost $0.15 per query when processing 5,000 input tokens now costs just $0.02 per query after caching optimization—an 87% cost reduction that compounds across thousands of daily requests.
Strategy 2: Batch API for Asynchronous Processing (50% Savings)
The Batch API offers a straightforward 50% discount on both input and output tokens for workloads that don't require real-time responses. This brings GPT-5.2 costs down to $0.875 per million input tokens and $7 per million output tokens—making it one of the most impactful optimizations for appropriate use cases.
Batch processing works by allowing you to submit large collections of API requests for asynchronous processing, with OpenAI guaranteeing completion within a 24-hour window. The service reads request details from a pre-uploaded file, processes them in optimized batches on their infrastructure, and writes responses to an output file that you retrieve once processing completes. This approach enables OpenAI to schedule your requests during lower-demand periods, passing the infrastructure savings directly to you.
The ideal use cases for batch processing include any non-time-sensitive workload where users don't need immediate responses. Content generation pipelines that prepare articles, product descriptions, or marketing materials in advance benefit enormously from batch processing. Data enrichment tasks that add AI-generated metadata, summaries, or classifications to existing datasets fit perfectly. Bulk analysis operations that process historical data, generate reports, or evaluate large document collections can run overnight at half the cost. Even email or notification generation systems that prepare personalized messages for delivery at scheduled times should leverage batch processing.
pythonimport json
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
# Prepare batch input file
batch_requests = []
for i, document in enumerate(documents_to_process):
batch_requests.append({
"custom_id": f"doc-{i}",
"method": "POST",
"url": "/v1/chat/completions",
"body": {
"model": "gpt-5.2",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "Summarize the following document concisely."},
{"role": "user", "content": document}
],
"max_tokens": 500
}
})
# Write requests to JSONL file
with open("batch_input.jsonl", "w") as f:
for request in batch_requests:
f.write(json.dumps(request) + "\n")
# Upload and create batch
batch_file = client.files.create(file=open("batch_input.jsonl", "rb"), purpose="batch")
batch_job = client.batches.create(
input_file_id=batch_file.id,
endpoint="/v1/chat/completions",
completion_window="24h"
)
# Check status and retrieve results
status = client.batches.retrieve(batch_job.id)
print(f"Batch status: {status.status}")
# Status progression: validating -> in_progress -> finalizing -> completed
The batch API tracks jobs through several status states. Validating indicates the system is checking your input file format and content. In Progress means requests are actively processing. Finalizing shows that processing completed and results are being prepared. Completed confirms results are ready for download. The Expired status indicates the batch couldn't complete within the 24-hour SLA, while Canceling and Canceled reflect user-initiated termination.
Combining batch processing with intelligent scheduling yields additional benefits beyond the 50% discount. By accumulating requests over 5-15 minute windows rather than processing individually, you reduce API overhead and enable more efficient internal batching. Organizations implementing this pattern report an additional 20-30% efficiency gain on top of the base batch discount, bringing total savings to 60-65% compared to real-time processing.
Strategy 3: Intelligent Model Routing (40-70% Savings)
Perhaps the most architecturally significant optimization involves routing requests to the most cost-effective model capable of handling them. The GPT-5 family spans three tiers with dramatically different pricing: GPT-5 Full at $1.25/$10 per million tokens, GPT-5-Mini at $0.25/$2, and GPT-5-Nano at just $0.05/$0.40. For GPT-5.2 specifically, using GPT-5-Mini or GPT-5-Nano for appropriate tasks instead of the full model can reduce costs by 85-97%.
The key insight is that most production workloads contain a mix of task complexities. Simple classification tasks, entity extraction, and format validation don't require GPT-5.2's full reasoning capabilities. Moderate tasks like content generation, summarization, and standard Q&A perform excellently on GPT-5-Mini. Only complex reasoning, multi-step analysis, and mission-critical accuracy truly demand GPT-5.2 or GPT-5.2 Pro.
| Task Category | Recommended Model | Cost Savings vs GPT-5.2 |
|---|---|---|
| Classification, tagging | GPT-5-Nano | 97% |
| Content generation, summarization | GPT-5-Mini | 86% |
| Standard coding, analysis | GPT-5 | 29% |
| Complex reasoning | GPT-5.2 Thinking | Baseline |
| Mission-critical accuracy | GPT-5.2 Pro | -1100% (costs more) |
Microsoft's Azure AI Foundry demonstrates the power of intelligent routing through their model router feature, which uses a fine-tuned small language model to evaluate each prompt and automatically select the optimal model based on complexity, performance requirements, and cost efficiency. This automated routing achieves up to 60% inferencing cost savings with no measurable loss in output quality.
Implementing your own routing logic requires classifying incoming queries by complexity before dispatching to models. A practical approach starts with a lightweight classifier—potentially GPT-5-Nano itself—that evaluates query characteristics. Simple heuristics can also work: queries under 100 tokens with straightforward intent route to Nano; moderate-length queries without complex reasoning requirements route to Mini; queries involving multi-step reasoning, code generation, or specialized analysis route to GPT-5.2.
pythondef route_query(query: str, context: dict) -> str:
"""Route queries to cost-effective models based on complexity."""
# Simple heuristics for routing
query_length = len(query.split())
requires_reasoning = any(word in query.lower() for word in
['analyze', 'compare', 'evaluate', 'explain why', 'step by step'])
requires_code = any(word in query.lower() for word in
['code', 'function', 'implement', 'debug', 'refactor'])
if query_length < 50 and not requires_reasoning and not requires_code:
return "gpt-5-nano" # $0.05/$0.40 per 1M tokens
elif not requires_reasoning or (requires_code and 'complex' not in query.lower()):
return "gpt-5-mini" # $0.25/$2.00 per 1M tokens
elif requires_code or requires_reasoning:
return "gpt-5.2" # $1.75/$14.00 per 1M tokens
else:
return "gpt-5" # $1.25/$10.00 per 1M tokens
# Usage in production
model = route_query(user_query, request_context)
response = client.chat.completions.create(model=model, messages=messages)
One production team documented their migration results: switching from all-GPT-4o to a tiered GPT-5 family approach reduced monthly API costs from $3,200 to $1,100—a 66% reduction while actually improving output quality for complex tasks. The routing system directed lightweight queries to Nano, standard work to Mini, and complex problem-solving to GPT-5, ensuring each query received appropriate computational resources without overspending on simple tasks.
Strategy 4: Semantic Caching for Repetitive Queries (60-70% Savings)
While OpenAI's built-in prompt caching handles exact prefix matches, semantic caching takes optimization further by identifying conceptually similar queries and serving cached responses even when the exact wording differs. This technique proves particularly valuable for applications where users ask the same questions in different ways—which describes most customer-facing AI implementations.
Traditional exact-match caching stores and reuses identical prompt-response pairs, eliminating redundant API calls only when queries match character-for-character. Semantic caching uses vector embeddings to represent query meaning, enabling the system to recognize that "What's your return policy?" and "How do I return a product?" are asking the same thing. When similarity scores exceed a configured threshold, the cached response serves immediately without an API call.
Production systems implementing semantic caching report 40-60% cache hit rates depending on query diversity, with some highly structured applications like FAQ systems achieving 70%+ hit rates. At 60% cache hits, you're effectively reducing API costs by 60% for those queries—and when combined with prompt caching on misses, total savings compound dramatically.
The GPTCache library, fully integrated with LangChain and LlamaIndex, provides a production-ready semantic caching implementation. It supports multiple embedding models for similarity calculation, various vector storage backends including Redis and Faiss, and configurable similarity thresholds that let you balance cache hit rates against response accuracy.
pythonfrom gptcache import Cache
from gptcache.embedding import OpenAI as OpenAIEmbedding
from gptcache.similarity_evaluation import SearchDistanceEvaluation
from gptcache.manager import CacheBase, VectorBase
# Initialize semantic cache
embedding = OpenAIEmbedding()
cache_base = CacheBase("sqlite")
vector_base = VectorBase("faiss", dimension=embedding.dimension)
cache = Cache()
cache.init(
embedding_func=embedding.to_embeddings,
data_manager=get_data_manager(cache_base, vector_base),
similarity_evaluation=SearchDistanceEvaluation(),
)
def query_with_cache(query: str):
# Check semantic cache first
cached = cache.get(query)
if cached is not None:
return cached # Free response from cache
# Cache miss - call API
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": query}]
)
result = response.choices[0].message.content
# Store in cache for future similar queries
cache.set(query, result)
return result
Cache invalidation strategies require careful consideration with GPT-5.2's improved consistency. Time-based TTL policies should vary by content type: factual queries about stable information can cache for 24-48 hours, while time-sensitive topics need shorter windows. Creative outputs typically bypass cache entirely to ensure response diversity. Implementing smart invalidation based on source data changes—such as when your FAQ database updates—ensures cached responses remain accurate without unnecessary expiration.
Distributed caching using Redis or Memcached enables sharing cached responses across multiple application instances, multiplying the benefit of each cache hit. Cache warming strategies that preload common queries during off-peak hours ensure high hit rates from the first request of each business day. Combined with Portkey's semantic caching solution, which offers 90-day cache retention and sub-5ms lookup times, semantic caching becomes a cornerstone of cost-effective GPT-5.2 deployment.
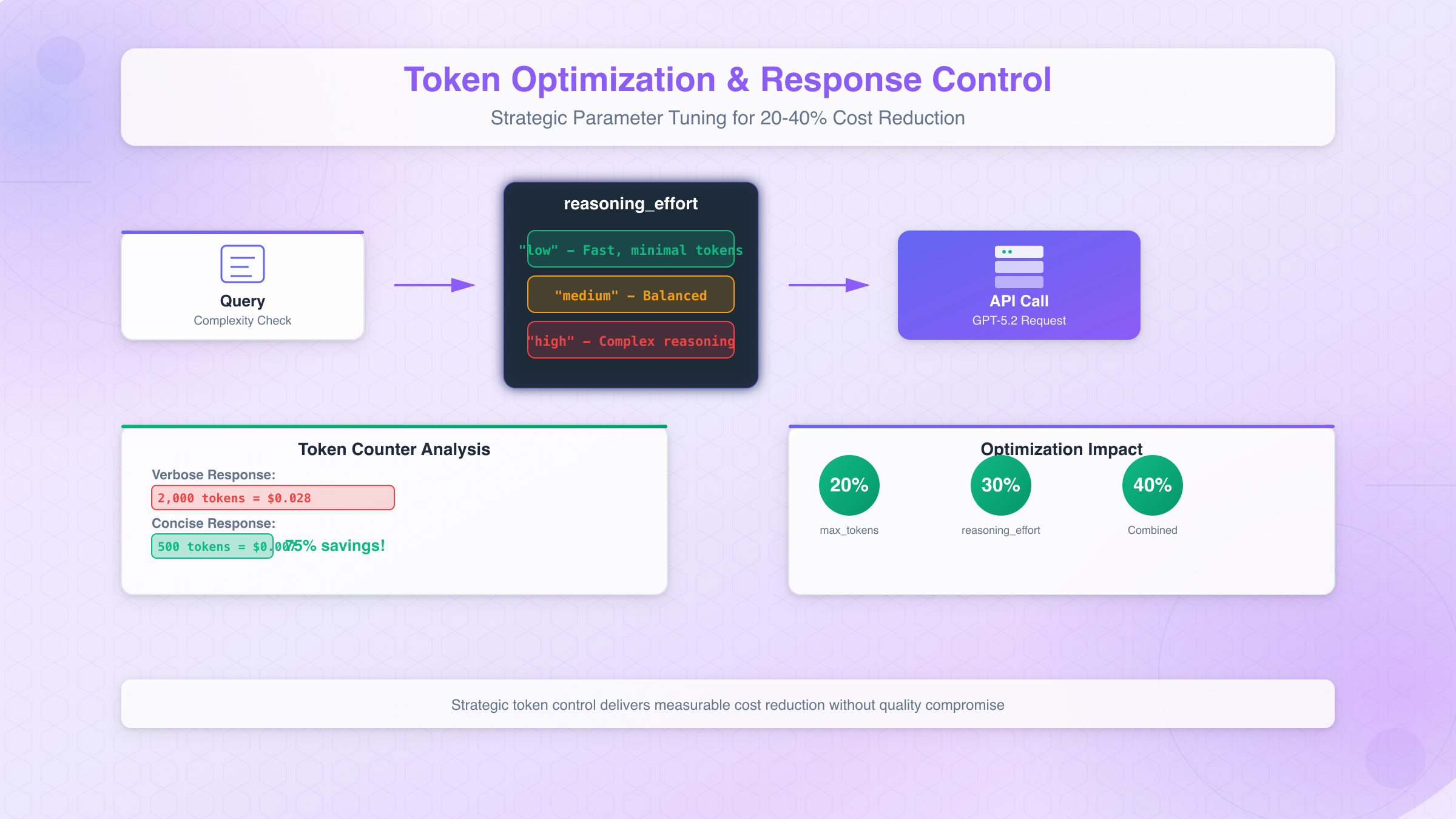
Strategy 5: Token Optimization and Response Control (20-40% Savings)
Beyond the major architectural optimizations, fine-tuning your token usage at the request level yields significant cumulative savings. Since output tokens cost 8x more than input tokens in GPT-5.2, controlling response length becomes a powerful cost lever. The difference between a 2,000-token response and a 500-token response translates to $0.021 in savings per request—which adds up to $21,000 saved per million requests.
GPT-5.2 introduces the reasoning_effort and verbosity API parameters that give developers explicit control over response characteristics. The reasoning_effort parameter accepts values of "low", "medium", or "high", directly affecting how much computational work the model performs on each request. For straightforward queries, setting reasoning_effort: "low" produces faster responses with fewer reasoning tokens, while reserving "high" for genuinely complex problems ensures you only pay premium reasoning costs when necessary.
The verbosity parameter similarly controls output length, ranging from "brief" to "detailed". A brief response for a simple factual query might use 100 tokens, while detailed mode could generate 1,000+ tokens for the same query. Training your team to match verbosity settings to actual requirements prevents the common pattern of over-generating content that users don't need.
python# Cost-optimized request configuration
def create_optimized_request(query: str, complexity: str = "low"):
config = {
"low": {"reasoning_effort": "low", "max_tokens": 500},
"medium": {"reasoning_effort": "medium", "max_tokens": 1000},
"high": {"reasoning_effort": "high", "max_tokens": 2000}
}
return client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": query}],
**config[complexity]
)
# Always set max_tokens to prevent runaway costs
response = create_optimized_request(
"Summarize this article in 3 bullet points",
complexity="low" # Simple task, minimal reasoning needed
)
Prompt engineering itself offers token savings opportunities. Removing redundant spaces and unnecessary formatting, using abbreviations where context permits, and stripping non-essential details from queries all reduce input token counts. Pre-processing user inputs to normalize whitespace and remove filler words can trim 10-15% from input tokens without affecting response quality.
Conversation history management presents another optimization avenue. Instead of sending the entire conversation context with each request, summarize earlier exchanges into a condensed context. A 20-message conversation history might consume 4,000 tokens when sent raw, but a well-crafted summary captures the essential context in 500 tokens—an 87.5% reduction in context costs per request.
Strategy 6: API Gateway Solutions for Enterprise Savings
For organizations processing substantial API volumes, dedicated API gateway services unlock cost reductions beyond what's achievable through direct OpenAI access alone. These platforms aggregate volume across multiple customers, negotiating enterprise-tier pricing that individual developers can't access directly. The resulting savings typically range from 30-70% compared to standard OpenAI rates.
laozhang.ai exemplifies this approach, offering intelligent multi-node routing that optimizes both cost and latency. The platform achieves 99.9% availability through geographic distribution while passing volume-based discounts directly to users. For a typical enterprise processing 500 million tokens monthly, the savings reach $15,000-20,000 compared to direct OpenAI pricing—funds that can instead fuel product development or expanded AI capabilities.
| Pricing Tier | Direct OpenAI | Via API Gateway | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-5.2 Input | $1.75/1M | $0.60-1.20/1M | 31-66% |
| GPT-5.2 Output | $14.00/1M | $4.90-9.80/1M | 30-65% |
| GPT-5 Input | $1.25/1M | $0.40-0.90/1M | 28-68% |
| GPT-5 Output | $10.00/1M | $3.50-7.00/1M | 30-65% |
The technical benefits extend beyond pricing. Gateway services typically offer built-in request queuing, automatic retry logic with exponential backoff, and response caching that operates across their entire customer base. When multiple users ask similar questions, the gateway's shared semantic cache can serve responses without hitting OpenAI's API at all—savings that would be impossible to achieve with individual direct connections.
Regional optimization becomes particularly valuable for global applications. API gateways maintain endpoints across multiple geographic regions, routing requests to the nearest node to minimize latency. For applications serving users in Asia, Europe, and the Americas, this distributed architecture can reduce response times by 40-60% compared to routing all traffic through a single OpenAI endpoint.
The implementation typically requires minimal code changes—usually just updating your base URL and API key configuration. Most gateway services maintain OpenAI API compatibility, meaning your existing code continues working with only the endpoint modification. This low-friction migration path makes gateway services an attractive option for teams seeking immediate cost reductions without architectural overhauls.
Strategy 7: Avoiding Common Cost Pitfalls
Even teams implementing the optimization strategies above can inadvertently drain their budgets through common anti-patterns. Understanding these pitfalls helps you avoid the hidden costs that accumulate silently until your monthly bill arrives.
The conversation history trap catches many developers by surprise. With each turn of a chat-based interaction, input token counts grow as previous messages accumulate in the context. A conversation that starts with a 500-token exchange can balloon to 5,000+ tokens by the tenth message—a 10x cost increase that compounds with every additional turn. Implementing conversation summarization or context windowing prevents this exponential growth.
Retry loop spirals occur when failed API calls trigger automatic retries without proper backoff logic. A single failed request can spawn 5-10 retry attempts in rapid succession, each incurring charges regardless of success. Implementing exponential backoff with jitter ensures retries space out appropriately, while circuit breaker patterns prevent runaway retry costs during API outages. For comprehensive guidance on handling rate limits and retry strategies, see our API rate limits guide.
The missing max_tokens parameter causes silent budget overruns. Without explicit limits, models generate responses as long as they deem appropriate—which often means verbose explanations when a sentence would suffice. Always set max_tokens to the minimum value that meets your requirements. For classification tasks, 50 tokens often suffices. For summaries, 500 tokens handles most cases. Only content generation tasks genuinely need 1,000+ token limits.
Over-specifying model requirements wastes money on capabilities you don't use. Teams default to GPT-5.2 for everything when GPT-5-Mini handles 80% of their queries equally well. Conduct an audit of your actual query types—you'll likely find substantial portions that don't require frontier model capabilities.
python# Anti-pattern: No limits, no routing
# This request could cost $0.05 or $0.50 depending on response length
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2", # Most expensive option
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Is this email spam?"}]
# No max_tokens = unbounded response length
)
# Optimized: Appropriate model, bounded response
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5-nano", # 97% cheaper for simple classification
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Is this email spam? Reply only 'spam' or 'not spam'."}],
max_tokens=10 # Classification needs minimal tokens
)
Ignoring error handling costs leads to wasted spend on requests that won't succeed. API errors typically occur on 2-3% of requests, and without proper handling, these failures consume tokens while delivering no value. Implement comprehensive error handling that logs failures for analysis without blindly retrying requests that will continue failing.
The development environment oversight catches teams who forget to separate testing from production. Using GPT-5.2 for development and debugging when GPT-5-Nano would suffice burns through budget without business benefit. Configure separate API keys or routing rules for development environments that default to lower-cost models.
Strategy 8: Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
Transforming your GPT-5.2 integration from cost-center to cost-optimized requires a systematic approach. Rather than attempting all optimizations simultaneously, prioritize changes by impact-to-effort ratio and implement incrementally.
Week 1-2: Quick Wins Start with zero-code changes that deliver immediate results. Set billing alerts and spending limits in your OpenAI dashboard to prevent surprise overages. Audit your current usage patterns to identify which queries dominate your token consumption. Enable usage tracking to establish baseline metrics for measuring improvement.
Week 3-4: Response Optimization
Add max_tokens parameters to all API calls based on actual response length requirements. Implement the reasoning_effort parameter, defaulting to "low" and escalating only when needed. These changes typically require minimal code modifications but yield 20-30% savings.
Week 5-6: Model Routing Deploy a routing layer that directs queries to appropriate model tiers. Start with simple heuristics based on query length and keyword detection. Monitor routing decisions and refine rules based on actual performance data. This phase often delivers the largest single cost reduction—40-70% for mixed workloads.
Week 7-8: Caching Implementation Integrate semantic caching for repetitive query patterns. Configure cache TTLs based on content freshness requirements. Implement cache warming for predictable high-volume queries. The combination of OpenAI's prompt caching and your semantic cache layer compounds savings effectively.
For teams seeking maximum optimization with minimal implementation effort, laozhang.ai provides a unified API gateway that bundles many of these optimizations automatically. The platform offers intelligent request routing, built-in caching, and volume-based discounts through a single integration point. New users receive a $100 credit bonus, enabling risk-free evaluation of the platform's cost-saving capabilities before committing to migration.
| Implementation Phase | Expected Savings | Effort Level |
|---|---|---|
| Response limits & controls | 20-30% | Low |
| Model routing | 40-70% | Medium |
| Prompt caching optimization | 30-50% | Low |
| Semantic caching | 40-60% | Medium |
| API gateway integration | 30-70% | Low |
| Combined total | 70-85% | Varies |
Monitoring and Continuous Optimization Cost optimization isn't a one-time project but an ongoing practice. Configure dashboards that track token consumption by model, request type, and user segment. Set up alerts when spending patterns deviate from baselines. Review monthly cost reports to identify new optimization opportunities as usage patterns evolve.
The most cost-effective GPT-5.2 deployments share common characteristics: they match model capabilities to actual task requirements, leverage caching aggressively for repetitive patterns, batch non-urgent workloads, and monitor costs as carefully as they monitor performance. By implementing these eight strategies systematically, you can reduce GPT-5.2 API costs by 50-80% while maintaining—or even improving—the quality your users experience.

Frequently Asked Questions
What's the fastest way to reduce GPT-5.2 costs without code changes? Enable OpenAI's automatic prompt caching by structuring prompts with static content at the beginning. This alone can reduce input costs by up to 90% for repetitive queries with shared context.
Should I use GPT-5.2 or stick with GPT-5 for cost savings? It depends on your accuracy requirements. GPT-5.2's improved token efficiency often makes the cost per quality-adjusted output lower than GPT-5, despite higher per-token pricing. For simple tasks, GPT-5-Mini or Nano deliver better value than either.
How much can I realistically save with these optimizations? Most organizations achieve 50-70% cost reductions through comprehensive optimization. Teams processing high volumes with repetitive query patterns often exceed 80% savings by combining prompt caching, model routing, and semantic caching.
Is using an API gateway worth the vendor dependency? For organizations processing more than 10 million tokens monthly, gateway services typically pay for themselves within the first month through volume discounts. The key is ensuring the gateway maintains OpenAI API compatibility for easy migration if needed.
How do I track whether my optimizations are working?
Monitor the usage field in API responses, which reports both prompt_tokens and completion_tokens. Track cached_tokens separately to measure prompt caching effectiveness. Build dashboards that show cost trends by model and request type over time.