Claude Opus 4.5 Price Guide 2025: Complete API Pricing, Cost Calculator & Optimization Tips
Comprehensive guide to Claude Opus 4.5 pricing: $5/$25 per million tokens, 67% cheaper than Opus 4.1. Includes cost comparison with GPT-5.1 and Gemini 3, prompt caching savings, batch discounts, and real-world cost calculations.
Nano Banana Pro
4K图像官方2折Google Gemini 3 Pro Image · AI图像生成
The New Economics of AI's Most Capable Model
Claude Opus 4.5 price represents a watershed moment in AI economics. Anthropic's flagship model now costs just $5 per million input tokens and $25 per million output tokens—a stunning 67% reduction from its predecessor, Opus 4.1, which demanded $15 and $75 respectively. This dramatic price cut fundamentally changes the calculus for developers, enterprises, and AI enthusiasts who previously found top-tier Claude capabilities financially prohibitive.
The November 2025 release of Claude Opus 4.5 brought more than just improved benchmarks. While the model achieves an impressive 80.9% on SWE-bench Verified (making it the current leader in real-world software engineering tasks) and outperforms human engineers in many coding benchmarks, the pricing restructure arguably matters more to practical adoption. At $5/$25 per million tokens, sophisticated AI applications that once required careful cost-benefit analysis now become economically viable for a far broader range of use cases.
This pricing shift reflects broader competitive pressures in the AI market. OpenAI's GPT-5.1 offers even lower base rates at $1.25/$10 per million tokens, while Google's Gemini 3 Pro sits at $2/$12. Yet raw token pricing tells only part of the story—Claude Opus 4.5's token efficiency, particularly with its new effort parameter, often results in comparable or lower total costs for complex tasks despite higher per-token rates. Understanding these nuances separates informed API consumers from those who simply chase the lowest headline numbers.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will dissect every aspect of Claude Opus 4.5 pricing: from base API costs and prompt caching strategies that can slash expenses by up to 90%, to batch processing discounts and real-world cost calculations for various use cases. Whether you're evaluating a switch from GPT-5.1, migrating from Claude Opus 4.1, or selecting your first frontier AI model, the data and analysis here will equip you to make financially sound decisions.

Complete Pricing Breakdown: Every Cost You Need to Know
Understanding the full Claude Opus 4.5 pricing structure requires examining multiple tiers and options. The base rates serve as starting points, but sophisticated users leverage caching, batching, and other mechanisms to dramatically reduce actual costs.
Base API Pricing
The foundation of Claude Opus 4.5 pricing consists of two primary rates. Input tokens—encompassing your prompts, system messages, and conversation history—cost $5 per million tokens. Output tokens—the model's generated responses—cost $25 per million tokens. This 5:1 ratio between output and input pricing reflects the significantly higher computational resources required for generation versus processing.
For context, one million tokens represents approximately 750,000 English words. A typical conversational exchange might involve 500-1,000 input tokens and 300-800 output tokens, costing fractions of a cent per interaction. The economics become more significant at scale: processing 100 million tokens monthly translates to $500 in input costs and potentially $2,500 in output costs depending on response lengths.
The model identifier for API calls is claude-opus-4-5-20251101, and Claude Opus 4.5 offers a 200,000 token context window with a maximum output of 64,000 tokens per response. These specifications enable handling entire codebases, lengthy documents, or extended multi-turn conversations within a single context—capabilities that justify premium pricing for appropriate use cases.
Complete Pricing Table: All Claude Models
| Model | Input ($/MTok) | Output ($/MTok) | Context Window | Max Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claude Opus 4.5 | $5.00 | $25.00 | 200K | 64K |
| Claude Opus 4.1 | $15.00 | $75.00 | 200K | 32K |
| Claude Sonnet 4.5 | $3.00 | $15.00 | 200K | 64K |
| Claude Haiku 4.5 | $1.00 | $5.00 | 200K | 64K |
| Claude Haiku 3.5 | $0.80 | $4.00 | 200K | 8K |
The table reveals important patterns. Claude Opus 4.5 costs 67% less than its predecessor while offering double the maximum output tokens. Meanwhile, Sonnet 4.5 at $3/$15 provides a middle ground for users who need strong capabilities without Opus-level reasoning, and Haiku 4.5 at $1/$5 serves high-volume, latency-sensitive applications where speed matters more than depth.
Prompt Caching: Up to 90% Savings
Prompt caching transforms Claude Opus 4.5 economics for applications with repetitive context patterns. When you cache frequently-used prompts, system instructions, or reference materials, subsequent requests read from cache rather than reprocessing the same tokens.
| Cache Duration | Write Cost | Read Cost | Effective Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 minutes | $6.25/MTok | $0.50/MTok | 90% on reads |
| 1 hour | $10.00/MTok | $0.50/MTok | 90% on reads |
The mechanics work as follows: cache writes cost a premium (1.25x for 5-minute TTL, 2x for 1-hour TTL) to store the processed tokens. However, cache reads cost just $0.50 per million tokens—a 90% discount versus standard input pricing. Applications that repeatedly use the same system prompts, documentation, or context see dramatic savings once the initial cache write amortizes across many requests.
Consider a customer service application with a 5,000-token system prompt defining product information and response guidelines. Without caching, every API call pays $0.025 for those tokens. With caching, the first call pays $0.03125 (cache write), but all subsequent calls within the TTL pay just $0.0025—ten times cheaper. After just two requests, caching pays for itself.
Batch Processing: 50% Discount for Asynchronous Workloads
For non-time-sensitive tasks, the Batch API provides substantial savings. Batch processing reduces both input and output costs by 50%, making it ideal for content generation pipelines, dataset analysis, bulk classifications, and other workloads where immediate responses are unnecessary.
| Pricing Type | Input ($/MTok) | Output ($/MTok) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard API | $5.00 | $25.00 |
| Batch API | $2.50 | $12.50 |
Batch requests accept up to 10,000 requests per batch with results delivered within 24 hours (often much faster). This model suits overnight processing jobs, weekly report generation, or any pipeline that can tolerate latency in exchange for cost savings. Organizations processing millions of tokens monthly often route non-urgent workloads through batch endpoints automatically.
Combined Savings: The 95% Reduction Path
The most aggressive cost optimization combines batch processing with 1-hour prompt caching. In this configuration, cache reads cost just $0.50 per million tokens through batch endpoints (technically $0.25 with the 50% batch discount), approaching the theoretical floor for Claude Opus 4.5 access. While this requires careful architecture to align cached prompts with batched workflows, high-volume applications achieve up to 95% cost reduction versus standard real-time API calls.
Price Comparison: Claude Opus 4.5 vs GPT-5.1 vs Gemini 3 Pro
Selecting an AI model involves more than comparing base token prices. True cost-effectiveness depends on task requirements, token efficiency, context needs, and available optimizations. This section provides the data needed for informed cross-model comparisons.
Direct Pricing Comparison
| Model | Input ($/MTok) | Output ($/MTok) | Context Window | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claude Opus 4.5 | $5.00 | $25.00 | 200K | Effort parameter, best coding |
| GPT-5.1 | $1.25 | $10.00 | 128K | Lowest raw price |
| Gemini 3 Pro | $2.00 / $4.00 | $12.00 / $18.00 | 200K / 1M | Tiered by context size |
At first glance, GPT-5.1 appears substantially cheaper—input tokens cost 75% less than Claude Opus 4.5. However, this analysis misses crucial factors affecting total cost. For a deeper comparison of these models' capabilities, see our detailed GPT-5.1 vs Claude 4.5 comparison.
The pricing differential narrows or reverses under several conditions. Claude Opus 4.5's effort parameter allows developers to match Sonnet 4.5's performance using 76% fewer output tokens at medium effort, or exceed Sonnet 4.5 by 4.3 percentage points using 48% fewer tokens at high effort. For complex reasoning tasks where multiple GPT-5.1 calls might be needed to match a single Claude Opus 4.5 response, the headline price advantage evaporates.
Gemini 3 Pro introduces contextual complexity with tiered pricing. Standard rates ($2/$12) apply for contexts up to 200,000 tokens, but larger contexts (Gemini supports up to 1 million tokens) incur premium rates of $4/$18 per million tokens. Applications requiring massive context windows find Gemini's pricing structure either compelling or prohibitive depending on their specific needs.
Price-Performance Analysis
Raw benchmarks provide context for pricing decisions. On SWE-bench Verified, Claude Opus 4.5 achieves 80.9%, compared to GPT-5.1's 77.9% and Gemini 3 Pro's 76.2%. For software engineering tasks specifically, the additional capability may justify the price premium.
| Benchmark | Claude Opus 4.5 | GPT-5.1 | Gemini 3 Pro |
|---|---|---|---|
| SWE-bench Verified | 80.9% | 77.9% | 76.2% |
| ARC-AGI (reasoning) | 35% | 38% | 45% |
| MMLU (knowledge) | ~91% | ~91% | ~91% |
| Terminal Bench | Best | Good | Good |
The picture varies by task type. Gemini 3 Pro dominates complex logical reasoning (45% on ARC-AGI with Deep Think mode), while general knowledge (MMLU) shows near-parity across all three. Claude Opus 4.5 particularly excels in agentic tasks, autonomous coding, and sustained multi-step reasoning—areas where its premium pricing often delivers corresponding value.
When Each Model Offers Best Value
Choose Claude Opus 4.5 when: Your application involves complex coding tasks, multi-step agentic workflows, or scenarios requiring exceptional token efficiency. The effort parameter makes it cost-competitive for tasks where other models require multiple attempts. For comprehensive feature analysis, explore our Claude Opus 4.5 vs Gemini 3 comparison guide.
Choose GPT-5.1 when: You're processing high volumes of straightforward queries, building conversational interfaces prioritizing cost over capability peaks, or operating within tight budgets. The raw price advantage matters most for simpler interactions at massive scale.
Choose Gemini 3 Pro when: Your use case requires processing extremely long documents (500K+ tokens), multimodal capabilities (images, video), or the most challenging logical reasoning problems. The context window advantage becomes decisive for document analysis applications.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Maximum Savings
Beyond model selection, implementation choices dramatically affect actual costs. These strategies apply specifically to Claude Opus 4.5 but parallel approaches exist for competing models.
Strategy 1: Implement Prompt Caching Systematically
Prompt caching delivers the highest ROI for applications with repetitive elements. Identify cacheable components in your implementation: system prompts, documentation blocks, few-shot examples, and any static context that appears across multiple requests.
The implementation requires restructuring API calls to separate cached and dynamic content. For Claude Opus 4.5, specify the cache_control parameter with either "ephemeral" (5-minute) or "persistent" (1-hour) TTL based on your access patterns. Applications typically see 60-90% input cost reduction after proper cache implementation.
Calculate your expected savings: if 70% of your average input tokens are cacheable and you make 1,000 daily requests, caching transforms those 700,000 tokens from $3.50 daily input cost to approximately $0.35 for cache reads plus amortized write costs—an 80%+ reduction.
Strategy 2: Route Non-Urgent Workloads to Batch API
Audit your current API usage to identify batch-eligible workloads. Common candidates include overnight content generation, weekly summary reports, bulk data classification, SEO content pipelines, and any processing that accepts multi-hour latency. Converting even 30% of API calls to batch endpoints yields 15% overall cost reduction with zero capability compromise.
The Batch API particularly benefits organizations with predictable, scheduled processing needs. A marketing team generating 500 product descriptions weekly saves 50% on that workload by submitting batch requests Sunday night for Monday morning delivery.
Strategy 3: Leverage the Effort Parameter
Claude Opus 4.5's effort parameter provides unprecedented control over the reasoning-cost tradeoff. The parameter accepts three values: "low," "medium," and "high." Each level adjusts how thoroughly the model explores solution spaces, directly impacting both quality and token consumption.
For routine queries where Sonnet-level reasoning suffices, medium effort matches Sonnet 4.5's best performance using 76% fewer output tokens. This effectively makes Opus 4.5 cost-competitive with Sonnet for straightforward tasks while preserving the option to escalate to high effort for genuinely challenging problems.
Implement adaptive effort selection based on query classification. Simple factual questions receive low effort; standard coding tasks get medium; complex debugging or architectural planning warrants high effort. This dynamic approach optimizes costs while maintaining quality where it matters.
Strategy 4: Optimize Context Management
Token costs accumulate from conversation history, system prompts, and reference materials. Aggressive context management reduces input tokens without sacrificing conversation coherence.
Implement conversation summarization that periodically condenses chat history while preserving essential context. Prune system prompts to eliminate redundancy. Use vector databases to retrieve relevant context dynamically rather than including entire knowledge bases in every request. These optimizations typically reduce input tokens by 30-50% for conversational applications.
For developers seeking additional cost reduction through alternative API access, services like laozhang.ai provide transparent pricing structures with competitive rates, particularly useful for teams requiring reliable access at scale or those operating in regions with limited direct API availability.
Real-World Cost Calculations: From Tokens to Budgets
Abstract pricing per million tokens means little without concrete applications to real workloads. This section translates Claude Opus 4.5 pricing into monthly budgets across typical use cases, enabling accurate financial planning.
Understanding Token Economics
Before calculating costs, establish conversion fundamentals. English text averages approximately 1.33 tokens per word, meaning 1,000 words consume roughly 1,330 tokens. Code typically runs slightly higher due to syntax and formatting characters—expect 1.5-2 tokens per word equivalent in most programming languages.
The input-output distinction matters significantly for budgeting. A prompt requesting a 500-word summary of a 2,000-word document involves approximately 2,660 input tokens ($0.0133) and 665 output tokens ($0.0166), totaling about $0.03 per request. These micro-costs compound at scale: 1,000 daily requests of this type cost $30 daily or $900 monthly at standard rates.
Monthly Cost Scenarios
The following scenarios represent common usage patterns with realistic token volumes. Actual costs vary based on specific prompt structures, response lengths, and optimization implementation.
| Usage Level | Daily Requests | Avg Input | Avg Output | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light (Individual) | 50 | 1,500 | 800 | ~$45 |
| Moderate (Team) | 500 | 2,000 | 1,200 | ~$525 |
| Heavy (Enterprise) | 5,000 | 3,000 | 1,500 | ~$6,000 |
| High-Volume | 50,000 | 2,500 | 1,000 | ~$50,000 |
These figures assume standard API pricing without caching or batching optimizations. Implementing the strategies discussed earlier reduces these costs by 50-90% depending on workload characteristics and architecture investments.
Use Case: Software Development Team
A ten-person development team using Claude Opus 4.5 for code review, debugging assistance, and documentation generates substantial API activity. Research indicates such teams average 200-400 API calls daily, with coding tasks requiring longer context windows than typical conversational use.
Assume average inputs of 4,000 tokens (code context plus query) and outputs of 2,000 tokens (detailed explanations and code suggestions). Daily token consumption reaches approximately 1.6 million input tokens and 800,000 output tokens. At standard rates, this calculates to $8 input plus $20 output—$28 daily or $840 monthly.
With systematic prompt caching of common code patterns, documentation, and coding guidelines, input costs drop by 70-80%. The team's effective monthly cost reduces to approximately $350-500, representing exceptional value for Opus-level coding assistance serving ten developers.
Use Case: Content Generation Pipeline
A marketing operation producing 500 product descriptions weekly presents different economics. Each description requires moderate input (product specifications, brand guidelines, style examples: ~2,500 tokens) and generates 400-600 words of output (~600 tokens). Weekly totals reach 1.25 million input tokens and 300,000 output tokens.
Standard pricing produces weekly costs of $6.25 (input) plus $7.50 (output) = $13.75, or approximately $55 monthly. However, content pipelines represent ideal batch API candidates—scheduling generation overnight reduces costs to $27.50 monthly, nearly 50% savings with zero quality impact.
Use Case: Customer Service Automation
High-volume customer service applications demand careful cost modeling. A support system handling 2,000 daily conversations averages 3-5 exchanges per conversation, with each exchange involving 500-800 input tokens and 200-400 output tokens. Conservative estimates suggest 5 million input tokens and 2 million output tokens daily.
At standard rates, daily costs reach $25 (input) plus $50 (output) = $75, translating to $2,250 monthly. This use case benefits enormously from prompt caching—the system prompt, product knowledge base, and response templates repeat across every conversation. After implementing 1-hour caching, input costs plummet by 85-90%, dropping monthly expenses to approximately $600-800 while maintaining identical service quality.
Cost Projection Calculator
For custom scenarios, apply this formula:
Monthly Cost = [(Daily Input Tokens × $5 / 1,000,000) + (Daily Output Tokens × $25 / 1,000,000)] × 30
Then apply relevant discounts: multiply by 0.5 for batch-eligible workloads, multiply input portion by 0.1 for highly cacheable prompts. Most production applications fall somewhere between these extremes—a 40-60% overall reduction represents realistic expectations for teams investing in optimization.

Subscription Plans vs API Access: Which Path Makes Sense?
The API pricing discussed throughout this guide represents one access method. Anthropic also offers subscription-based access through Claude.ai, creating a choice that depends on usage patterns, integration requirements, and budget constraints.
Consumer and Pro Subscriptions
Individual users access Claude Opus 4.5 through subscription tiers rather than direct API payments. The Free tier provides limited access to Haiku and Sonnet models only—Opus 4.5 requires a paid subscription. The Pro plan at $20 per month (or $17 annually) unlocks full Claude Opus 4.5 access through the Claude.ai interface, along with Claude Code integration and file execution capabilities.
For casual users making 50-100 queries daily, Pro subscriptions often prove more economical than API access. The subscription effectively provides unlimited conversations (within fair use limits) for a fixed monthly cost, eliminating the anxiety of per-token billing. However, subscription access lacks programmatic integration—you cannot build applications or automate workflows on subscription access alone.
The Max plan at $100 per month serves power users requiring 5-20x the usage limits of Pro. This tier targets professionals whose daily Claude usage approaches what would cost $200-500 through API pricing, making the flat fee substantially cheaper despite the higher sticker price. Max also includes conversation memory across sessions, enabling more sophisticated multi-day workflows.
Team and Enterprise Options
Organizations face additional considerations. Team Standard pricing starts at $30 per seat monthly with a five-seat minimum, providing shared workspace features, usage analytics, and administrative controls absent from individual plans. The team environment enables collaboration on prompts and outputs while maintaining security boundaries.
Team Premium at $150 per seat monthly adds enterprise requirements: SSO integration, audit logging, compliance certifications, and removal of Opus usage caps that constrain Standard tiers. Large organizations negotiating enterprise agreements typically achieve further discounts based on committed usage volumes, though specific rates require direct negotiation with Anthropic's sales team.
API vs Subscription Decision Framework
The optimal choice depends on three factors: integration requirements, usage volume, and cost predictability preferences.
Choose API access when: Your use case requires programmatic integration, you're building products or automations, usage patterns are predictable enough to estimate costs, or you need fine-grained control over model parameters (including the effort parameter). API access also enables batch processing and prompt caching optimizations unavailable through subscriptions. For teams building AI-powered applications, API access is effectively mandatory—subscriptions cannot power production systems.
Choose subscription access when: Your usage is primarily conversational through web or mobile interfaces, you prefer fixed monthly costs over variable usage-based billing, or you're an individual user without integration requirements. Subscriptions simplify budgeting and eliminate the overhead of API key management, usage monitoring, and billing reconciliation.
Consider both when: Some organizations maintain both access methods—subscriptions for ad-hoc employee use and API access for production systems. This hybrid approach captures the convenience of subscriptions for exploration while reserving API access for cost-optimized production workloads.
Migration from Opus 4.1: Quantifying the Upgrade Value
Organizations currently running Claude Opus 4.1 face a straightforward upgrade decision. The 67% price reduction alone justifies migration, but improved capabilities sweeten the economics further.
Direct Cost Comparison
The raw numbers speak clearly: Opus 4.1 at $15/$75 per million tokens versus Opus 4.5 at $5/$25 represents substantial savings at any scale. An organization processing 10 million input tokens and 5 million output tokens monthly saves $100 on inputs (from $150 to $50) and $250 on outputs (from $375 to $125)—a combined $350 monthly reduction with no capability loss.
| Monthly Volume | Opus 4.1 Cost | Opus 4.5 Cost | Monthly Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5M in / 2M out | $225 | $75 | $150 (67%) |
| 10M in / 5M out | $525 | $175 | $350 (67%) |
| 50M in / 20M out | $2,250 | $750 | $1,500 (67%) |
| 100M in / 50M out | $5,250 | $1,750 | $3,500 (67%) |
The percentage savings remain constant across scales because the discount applies uniformly to both input and output pricing. However, absolute dollar savings increase proportionally with volume, making the upgrade increasingly impactful for high-volume users.
Performance Improvements at Lower Cost
Beyond pricing, Opus 4.5 delivers measurable capability improvements. The SWE-bench Verified score increased from 74.5% (Opus 4.1) to 80.9% (Opus 4.5)—a 6.4 percentage point improvement in real-world software engineering tasks. This translates to higher success rates on complex coding tasks, potentially reducing the need for multiple attempts or manual intervention.
The effort parameter introduced in Opus 4.5 enables new optimization possibilities. Organizations can match Opus 4.1 performance levels using medium effort while consuming 48% fewer tokens—effectively doubling the price reduction for equivalent output quality. Teams willing to accept slightly reduced reasoning depth for routine tasks see 80%+ effective cost reductions compared to their current Opus 4.1 spending.
Maximum output capacity doubled from 32K to 64K tokens, eliminating truncation issues for users generating long-form content, detailed analyses, or comprehensive code reviews. This capability improvement alone may resolve pain points experienced with Opus 4.1's output limitations.
Migration Recommendations
The migration path is straightforward: update the model identifier from claude-opus-4-1-20250414 to claude-opus-4-5-20251101 in your API calls. No prompt modifications are required—Opus 4.5 maintains backward compatibility with existing prompt structures.
However, consider testing the effort parameter on representative workloads before full migration. Some applications may benefit from explicitly specifying medium effort for routine tasks, capturing additional savings beyond the baseline price reduction. Establish benchmarks comparing Opus 4.1 outputs against Opus 4.5 at various effort levels to identify optimal configurations for your specific use cases.
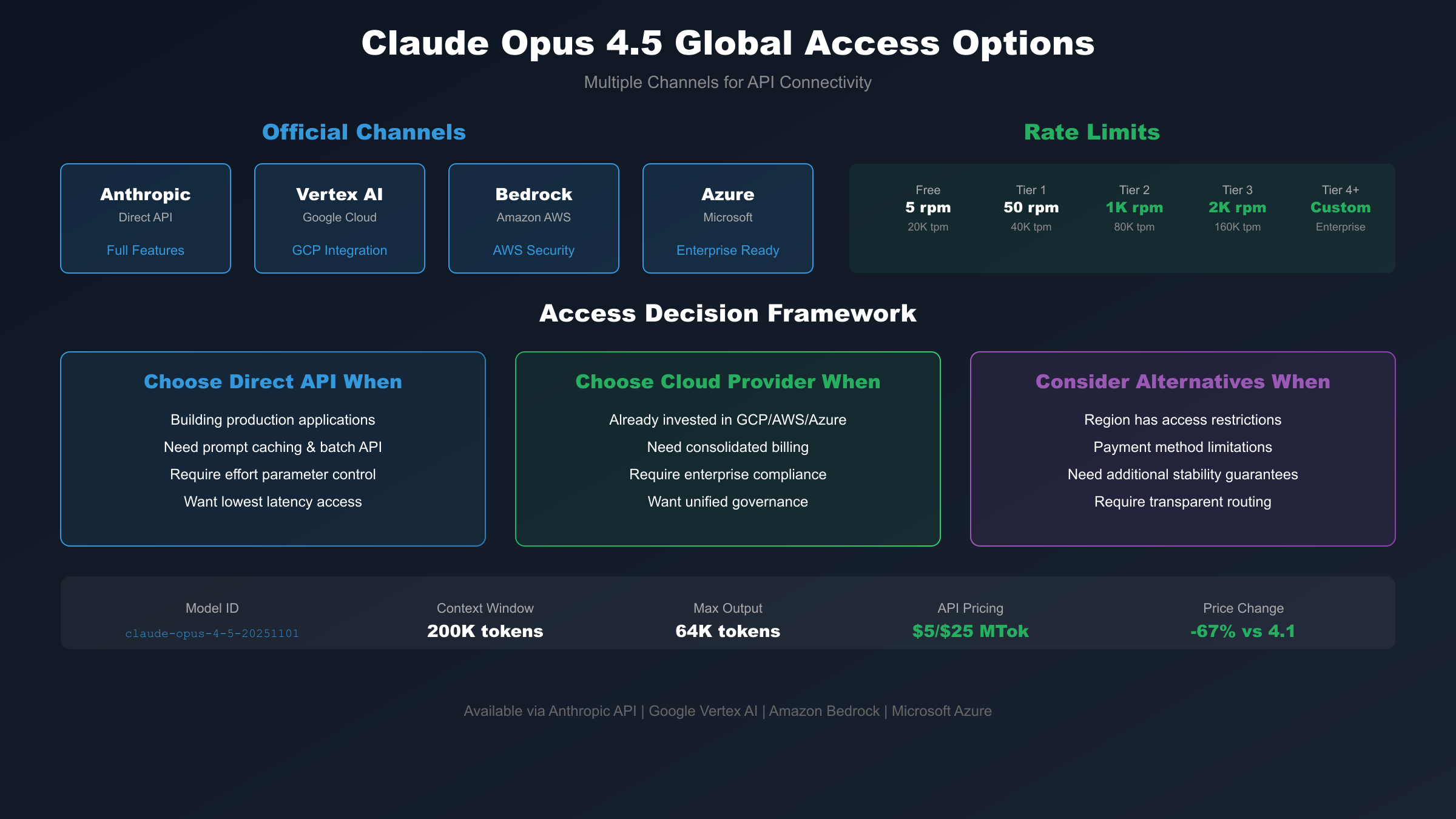
Global Access and Alternative Solutions
While Claude Opus 4.5 enjoys broad availability through multiple platforms, geographic and technical constraints affect some users. Understanding access options ensures uninterrupted service regardless of location or infrastructure requirements.
Official Availability Channels
Anthropic distributes Claude Opus 4.5 through several official channels. The Anthropic API provides direct access with full feature support, including prompt caching, batch processing, and all model parameters. This channel offers the lowest latency for users geographically proximate to Anthropic's infrastructure.
Google Cloud Vertex AI integrates Claude Opus 4.5 into Google's AI platform, enabling organizations already invested in Google Cloud to access Claude without additional vendor relationships. Vertex AI billing consolidates with existing Google Cloud invoices, simplifying procurement for enterprise customers.
Amazon Bedrock provides similar integration for AWS-centric organizations. Bedrock access includes AWS's security, compliance, and governance features, making it attractive for enterprises with strict infrastructure requirements. Both cloud provider integrations maintain pricing parity with direct Anthropic API access.
Microsoft Azure recently joined the distribution network, extending Claude availability to Azure customers. This expansion particularly benefits organizations with Microsoft-centric infrastructure or existing Azure AI services deployments.
Addressing Access Challenges
Users in certain regions face restrictions on direct API access due to regulatory requirements or infrastructure limitations. Payment processing challenges, particularly for users without US-issued credit cards, create additional friction. Network reliability issues in some areas result in inconsistent API response times that impact production applications.
For users facing such challenges, alternative API routing services have emerged to bridge access gaps. These services provide stable connectivity, alternative payment methods, and often include usage analytics and cost management tools beyond what direct API access offers. Users in regions with limited direct access particularly benefit from these intermediary services.
Services like laozhang.ai specialize in providing reliable Claude API access with transparent pricing, supporting users who require consistent connectivity regardless of geographic location. Such alternatives become particularly valuable for teams building production applications where API reliability directly impacts user experience and business continuity.
Rate Limits and Usage Tiers
API access includes rate limits that vary by usage tier. New accounts start with conservative limits that increase as usage history accumulates. Enterprise agreements typically include negotiated rate limits appropriate for production workloads.
| Tier | Requests/Minute | Tokens/Minute | Tokens/Day |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 5 | 20,000 | 300,000 |
| Tier 1 | 50 | 40,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Tier 2 | 1,000 | 80,000 | 2,500,000 |
| Tier 3 | 2,000 | 160,000 | 5,000,000 |
| Tier 4+ | Custom | Custom | Custom |
Organizations anticipating high-volume usage should plan for tier progression and consider enterprise agreements to ensure rate limits match production requirements from launch. Inadequate rate limits constrain application scalability regardless of budget allocation.
Is Claude Opus 4.5 Worth the Price? Final Assessment
After examining every dimension of Claude Opus 4.5 pricing—from base rates through optimization strategies to competitive positioning—the value proposition crystallizes clearly for different user profiles.
The 67% price reduction from Opus 4.1 removes the primary barrier that previously reserved Opus-class capabilities for well-funded projects. At $5/$25 per million tokens, Claude Opus 4.5 becomes economically viable for mainstream development teams, ambitious startups, and individual developers willing to invest in AI-augmented workflows. This accessibility expansion represents the pricing story's most significant implication.
For organizations already using Claude, the upgrade calculus is unambiguous. Equivalent capabilities at one-third the cost justify immediate migration. The effort parameter introduces additional optimization potential beyond raw price reduction, potentially halving effective costs for applications that can tolerate varying reasoning depth.
Compared to competitors, Claude Opus 4.5 occupies a premium position—more expensive than GPT-5.1 or Gemini 3 Pro on per-token basis, yet often cost-competitive on per-task basis due to superior token efficiency and first-attempt success rates. The choice depends on workload characteristics: straightforward high-volume queries favor cheaper alternatives, while complex reasoning and coding tasks often justify Claude's premium through reduced iteration.
The optimization toolkit—prompt caching, batch processing, effort parameter, and context management—transforms list prices into effective costs that approach or undercut competitors. Organizations investing in proper implementation routinely achieve 50-80% reductions from standard rates, making headline price comparisons misleading without considering achievable optimizations.
For detailed API pricing information across all Claude models, consult our comprehensive Claude API pricing guide. Teams evaluating Sonnet 4.5 as a cost-optimization alternative should review our Sonnet 4.5 pricing analysis for direct comparisons.
Getting started requires minimal investment: create an Anthropic account, generate an API key, and begin with the free tier to validate your use case. As usage scales, implement caching and batching optimizations progressively, monitoring costs through Anthropic's usage dashboard. For production applications requiring consistent global access, evaluate both direct API access and alternative providers to ensure reliability matches business requirements.
The Claude Opus 4.5 price point opens AI's most capable publicly available model to a vastly expanded audience. Whether that capability justifies its cost depends entirely on what you're building—but for complex tasks requiring nuanced reasoning, sophisticated coding, or sustained multi-step workflows, the investment frequently proves worthwhile.